
Phosphorus deficiency means that the body is not getting enough of this mineral. It can result in health complications and diseases, like arthritis, rickets, gum disease and more.
About phosphorus
Phosphorus is the second most abundantly found mineral in the human body, right after calcium. Both calcium and phosphorus are required for strong and healthy teeth and bones.
Phosphorus is required for proper functioning of kidneys, for the transmission of nerve impulses and for the utilization of fats, protein and carbohydrates. This mineral is a part of DNA and RNA and it helps in energy formation. Phosphorus is believed to be essential for good cell health, and therefore it speeds up healing of the wounds and injuries and prevents certain forms of cancer too.
Symptoms of phosphorus deficiency
About 85 percent of the phosphorus in the human body is found in the bones and the teeth, and the rest is distributed to blood, tissues, muscles and organs, especially brain and kidneys. It is also found in fluids in and around the cells. If there is not enough phosphorus in the body, it increases the risk of certain diseases.
Some of the symptoms of phosphorus deficiency include weak and brittle teeth and bones, general weakness, loss of appetite, tiredness, pain and stiffness in joints, confusion and susceptibility to infections.
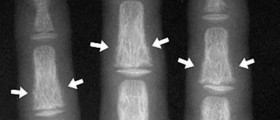
The imbalance in the calcium-phosphorus reserves in the body can lead to diseases like rickets (softening of the bones in children, possibly leading to deformities), arthritis, decaying teeth and pyorrhea (an advanced stage of periodontal disease).
Treatment for phosphorus deficiency
The recommended daily allowance of phosphorus is 1200 milligrams for adults, both male and female, and 800 milligrams for children. Phosphorus deficiency can be treated by taking adequate amounts of this mineral in the form of supplements and multivitamins, but also by eating foods rich in phosphorus.
Some of the best food sources of phosphorus include milk, yogurt, cheese, tuna fish, lobster, pork, pine nuts, sunflower seeds, bran flakes, peanut butter, bread (especially whole wheat), rice, corn, potatoes, broccoli, peas, sodas and milk chocolate.
Phosphorus found in foods of animal origin, such as dairy products, fish and meat, is much more easily and completely absorbed than the one found in vegetables, legumes and nuts.
Intake of other nutrients, especially calcium and vitamin D, should be adequate as well, because they have a direct bearing on the phosphorus in the body.
Having a well-balanced diet rich in all the essential nutrients and having regular check-ups at the doctor’s office are the best way to prevent phosphorus deficiency and health issues associated with it.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...