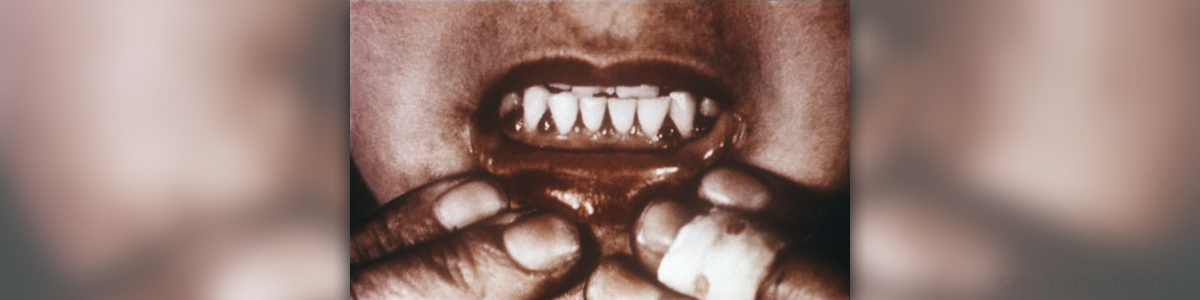
The gums or the gingivae are the fibrous tissue attached to the jaw bone. Healthy gums are at least 1mm thick with a normal blood flow that gives gums a red color.
Gum disease or periodontal disease involve bacterial growth or conditions that degenerate the gum tissue around the teeth.
Plaque is a normal presence on the surface of the teeth, caused by the presence of bacteria. Frequent brushing and flossing removes the plaque and prevents further complications. However, if plaque is not removed, it transforms into tartar or calculus. Tartar cannot be removed by normal brushing and requires a professional treatment.
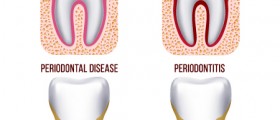
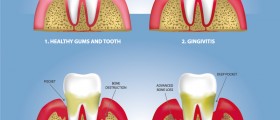
The gum disease has two phases, gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis usually comes first.
Symptoms of gingivitis are very red and swollen gums that bleed easily while brushing. If the plaque is not removed on time, it can progress to periodontitis.
Periodontitis starts with a greater amount of tartar that cannot be removed. The bacteria create waste products that destroy the gums and bones surrounding the teeth. The gum line moves upwards and pockets are formed that contain debris. If the plaque spreads 5mm deep or more, it is called moderate periodontal disease. As it progresses, more bone and tissue are affected, teeth become loose and may fall out. Also, bacteria release a sulphur compound that causes bad breath.
Since the pockets are not necessarily visible from the outside, X-rays or probing are used to detect their presence and progression.
Advanced periodontitis occurs when the pockets are more than 6mm deep. In this case, a surgery is necessary, during which the diseased tissue is removed, the surface of the tooth is completely cleaned and the gums are stitched around the teeth, usually lower that they were. If the disease has reached and affected the bone, a bone graft or restructuring will be necessary.
Gum abscess affects people whose bones around the tooth root are already damaged due to periodontal disease. The bacteria in the pockets change and new, more dangerous ones come in. Their waste products can lead to even more bone loss. The infection may even spread to neck and jaw.
Acute gum abscess causes pain, swelling and fever. Chronic abscess is usually painless and not easy to detect, as there are no apparent signs of its presence, unless an X-ray is performed.
It is important to know that brushing and flossing frequently and properly can prevent gum disease by removing its initial cause, the plaque. However, frequent visits to the dentist are also necessary, as a more in-depth examination of the teeth and gums will reveal the signs of the disease that may not always be visible.






,-Don't-Ignore-Receding-Gums_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...