
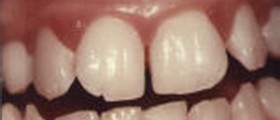
Mouth sores
They can be raised and filled with liquid, or ulcers, which are basically holes.
Causes of mouth sores
Mouth sores can be caused by injury or irritation. Most people have experienced painful sores after accidentally biting on their cheek. They can also be caused by poor-fitting dentures or a jagged tooth.
Allergic reactions can also cause mouth sores, if a person is allergic to an ingredient of a toothpaste, mouthwash, gum, candy and similar.
Virus infections are another common cause of mouth sores. They can be caused by herpes simplex virus, and in that case it is usually a cold sore on the lip, or by herpex zoster, which causes chickenpox and shingles.
Infections can also be caused by bacteria, most commonly spreading from an infected tooth, gums, or from the overgrowth of the bacteria that are normally present in the mouth.
Some diseases and disorders are known for causing mouth sores. Those include syphilis, Behcet’s syndrome, pemphigus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, celiac sprue, and others.
There is also a rare disease called necrotizing sialometaplasia in which a large, gapping sore is formed several days after an injury to the roof of the mouth. The sore may look frightening but it is usually painless and it heals without treatment in one to three months.
Treatment
Treatment for mouth sores depends on their underlying cause. Pain can be relieved by avoiding salty, acid foods, by using a soft toothbrush and mouthwashes with numbing effect. If the doctors are sure that the cause is not an infection, they may prescribe a corticosteroid ointment to be applied directly to each sore.
It is also possible to treat a mouth sore with laser or with locally applied silver nitrate.
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis or RAS is diagnosed in people who frequently have mouth ulcers or canker sores. They are usually triggered by stress, mouth injury or an allergy.
In people who have RAS mouth sores can appear few times a year or their outbreaks can be almost continuous. Pregnant women, women who take hormone-based oral contraceptives and people who use tobacco products for some reason are less prone to mouth sores.
Treatment usually consists in pain relievers and corticosteroid rinses.












_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...