Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is one of two very common types of lymphoma cancer. People who have this disease actually have a cancer of the lymphatic system, and in them, the disease develops in types of white blood cells known as lymphocytes, and spreads from one group of lymph nodes to another.
Even though the statistics prove that only 5 % of the people affected by this disease are children, the fact is that it can affect everyone, regardless of age and sex. The main symptoms of this disease are swollen yet painless lymph nodes in the neck, armpit or groins, and they are usually followed by fever, weight loss, itchy skin, coughing and fatigue.
As for the treatment of this disease, it depends on the type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, the stage at which the disease is discovered, the age of the patient and on the fact that lymphoma is indolent or aggressive. However, the treatment will probably consist of the transplantation of the stem cells, as well as chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In cases in which the disease is discovered at an early stage, the treatment shall last for a year approximately. It will probably consist of radiation therapy, which will be either external, meaning that it will be focused on the particular parts of the body, or internal, which means that radioactive substance will have to be injected in the center of the cancerous area. When the disease is discovered at the advanced stage, chemotherapy will probably be the recommended therapy. The side effects and complications of this therapy are very possible, given that it has a damaging impact on the patient's bone marrow. But one of the possibilities to avoid them includes removing and freezing the healthy stem cells from the blood and bone marrow, until the chemotherapy is completed, and then reinjecting them after that.
The studies and research are done in order to find the most effective cure for this disease, since not all the patients will react positively to these therapies, and not all of them will successfully fight this type of cancer.
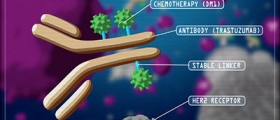
At some clinics, experimental therapies include biotherapy, in which antibodies are used in helping the immune system to destroy cancer cells, and radioimmunotherapy which is practically the ultimate solution, suggested to patients after all other solutions have failed in showing the results. Radioimmunotherapy drugs have the purpose to attach to cancer cells and destroy them by the amount of radiation that they contain. However, there is a good reason why this kind of therapy is not suggested at the beginning of the treatment. Even though the patients usually tolerates it well, sometimes it can lead to a fatal outcome, because it can cause infections, bleeding and reduce the number of blood cells.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...