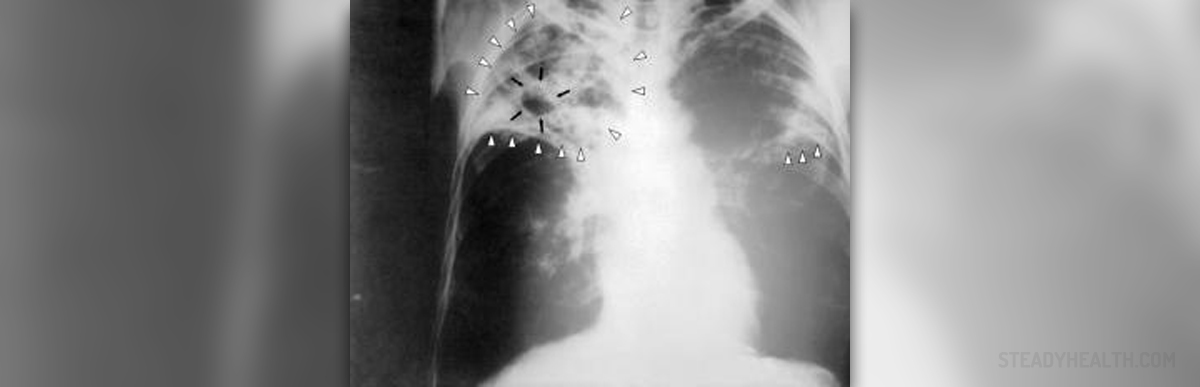
Information on Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis or shortened TB is an infectious disease that primarily attacks the lungs. The disease is caused by bacteria and it is infectious which means that the infection can be passed on to other people. Only the person who is definitely affected with tuberculosis can spread the infection to others through the air. When a sick person coughs, sneezes or just talks, he may pass the bacilli to others.However, that person can have bacilli but it is not certain that he will definitely immediately fall sick with TB. He or she may carry the bacilli inside without having TB symptoms. This is the case of latent TB. Apart from the lungs, tuberculosis may inflict the lymph nodes, the skin, the joints, urinary organs and nervous system. Proper and long-lasting treatment is of crucial importance for curing TB. The patient has to strictly follow the treatment procedures in order not to get further complications and thus reduce the risk of successful recovery. Treatment and Dosage
The dosage of medication given to the TB patients depends on the severity of symptoms and how much TB affected the lungs and the system. There are numerous medications, but antibiotics are primary medications, among which Pyrazinamide, Isoniazid, Rifampin, and Ethambutol are mostly used. Isoniazid and rifampin have proved effective in treating TB. Yet, some people may become resistant to them and therefore, pyrazinamide is added to the therapy. Isoniazid is recommended for people who are positive to TB but do not have any symptoms. The presence of TB can be revealed by doing tuberculin skin tests or having an x-ray of the lungs. If the tests turn positive, the person may be given Isoniazid for precarious measures. Also, those infected with HIV or diabetics can develop TB, which is why the medication can be given to them. Although the bacteria are resistant to isoniazid or rifampin, patients may use these medications to some extent due to their reactions to some other microorganisms. The medicines are combined with others, like e.g. streptomycin sulfate.
Warnings
The resistance to certain antibiotics may be due to some previous treatments with these medications (acquired resistance) or with no reasons (primary resistance). If a person has not stuck to the prescribed dosage and has not taken the medicine long enough, the bacteria survives and becomes resistant to the particular medicine when taken at the second round of treatment. Latent Tb can be cured after 6months of therapy, but patients with active TB may need more time, even years. For this reason it is crucial to be disciplined and not to stop the treatment.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...