Definition
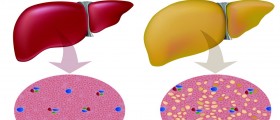
Liver is a vital organ in the body that has a wide range of functions including elimination of toxins and production of bile (concentrated fluid that digests the food in the intestines). In cases of fatty liver, or steatosis, problem is the build up of excessive fats in liver’s cells. Presence of fat in liver in relatively normal, but if exceeds 10% if total liver weight than it’s the case of fatty liver.
Causes
Causes of fatty liver can be attributed to several factors; one is obesity or overweight, other is steatohepatitis, which is liver inflammation due to fat accumulation, and the third is liver disorder due to excessive use of alcohol, and it is called alcoholic hepatitis. Unfortunately, hepatitis can occur also with the people who does not drink in which case disorder is called NASH or non alcoholic steatohepatitis. If untreated in time all these cases of liver disorders can lead to inflammation or other serious consequences.
Symptoms
Symptoms of fatty liver may include fatigue, malaise or a dull pain in the right upper abdomen. If there is an advance stage like cirrhosis, symptoms may be weakness, nausea, loss of weight, lack of appetite, etc.
Also the risk factors of liver disorders may be obesity, diabetes, some medications like Prednisone and others, etc.
Because the symptoms of fatty liver may be silent and unnoticeable, many cases are discovered during other body check ups. In case that your doctor finds that you have some type of fatty liver disorder, he may include additional tests, in order to establish the diagnose for sure, such as CT scan, MRI or ultrasound.
Treatments
Treatments in cases of fatty liver and steatohepatitis may include reduction of high blood triglycerides, losing extra weight, good diabetes control and abstain of alcohol. But regular medicine can only treat fatty liver and steatohepatitis symptoms and try to prevent any further complications. In some cases surgical procedure called intestinal bypass for obesity is required.
Also there are undergoing clinical trials for drug called Actigall. This drug appears to reduce liver damage in cases of fatty liver and steatohepatitis. But for now, real potential of this new drug is yet to be proved.
In cases of severe and chronic liver damage, liver transplantation is performed. Advances in surgical transplantation techniques and better understanding of drug suppressant is now enabling these procedures to become a standard in cases of fatty liver and steatohepatitis problems.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...