
This condition was once more dangerous than today. In the 1980s the mortality rate for mothers was as much as 85 percent, while today it is between 12,5 and 18 percent. Neonatal mortality rate is somewhat lower.
What is acute fatty liver of pregnancy?
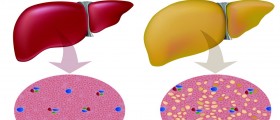
Fatty liver is characterized by microvesicular steatosis on the liver. Steatosis is basically abnormal accumulation of lipids within the cells. It is believed that the cause of this is improper oxidation of fatty acids, leading to acute liver insufficiency. This probably results from deficiency in the long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase (LCHAD) enzyme. It is a rare condition but potentially fatal. It usually occurs in the third trimester or immediately after the delivery of the baby.
The symptoms of acute fatty lover of pregnancy are non-specific and may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, weight loss, jaundice and fever.
In order to make a definitive diagnosis of acute fatty liver of pregnancy, it is necessary to do laboratory tests after the condition is suspected basing on the reported symptoms. The lab tests show abnormalities such as elevated liver enzymes, hypoglycemia, elevated white blood cell count and decreased fibrinogen.
Treatment for acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Once the diagnosis has been made, the only effective treatment for acute fatty liver in pregnancy is to deliver the baby, no matter what week of pregnancy the woman is in. The baby will probably show signs of asphyxia and hypoxia and will therefore need to be closely monitored. The cesarean section may be necessary if the delivery does not occur within the 24 hours after the diagnosis has been made. Pregnant women with acute fatty liver often have coagulation abnormalities, which means their coagulation factors will have to be replaced if the cesarean section turns out to be the only option.
Patients with AFLP need to be monitored closely because hypoglycemia may even lead to coma. Renal function must be controlled as well.
As for the surgical treatment, there is not one that is required or desired for patients with AFLP. In fact, due to coagulation problems, surgical interventions are performed only as the last resort. In addition, patients must be examined for genital lacerations due to vaginal delivery, in order to prevent or repair serious bleeding.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...