Herpes simplex virus (HSV) belongs to the family of Herpesviridae. There are two types of Herpes simplex virus that affect humans - herpes virus 1 and herpes virus 2, also known as HSV1 and HSV2. Other six types of HSV viruses do not cause any harm to people. The infection with HSV is highly contagious and it can lead to a number of different diseases. HSV has proven to be very likely to infect the skin and mucous membranes in the human body. It also affects the neurons of the dorsal root ganglia, where the virus persists for many years and cause latent infection.
HSV 1 and 2 Infections
Infection with HSV type 1 can cause: oral herpes, cold sores, herpes dermatitis, herpes keratitis and herpetic whitlow, but also genital and neonatal herpes and herpes encephalitis.
HSV 2 infections might lead to: neonatal and genital herpes, herpetic whitlow and herpetic dermatitis.
Oro-facial herpes or cold sores are in most cases caused by HSV1. Many people having problems with it acquired herpes infection when they were children, and the infection remain latent (present sometimes) all their life. It is usually associated with gingivostomatitis, fever and swelling of the lymph glands at the base of the jaw. This condition might even get serious, especially in immunocompromised or people with eczema.
HSV is also the main cause of keratitis and blindness worldwide. Therefore, ocular HSV infections must be treated in order to prevent the scarring.
Neonatal herpes affects the newborn babies, and can be acquired during the birth if the mother is infected with HSV but asymptomatic.
Genital herpes is one of the most transmitted STDs (sexually transmitted diseases), although it is often unrecognized and undiagnosed (in almost 80% of all cases).
HSV Diagnosis
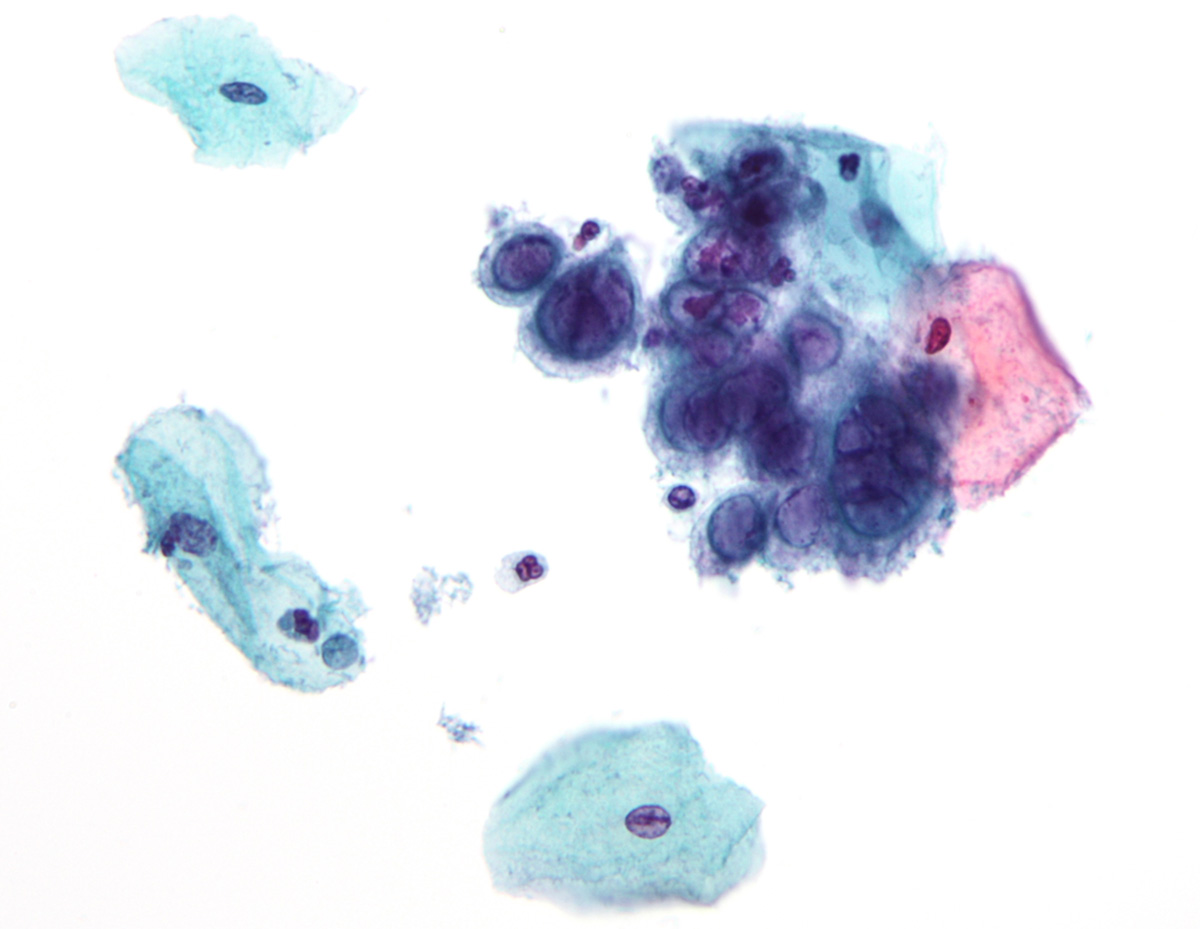
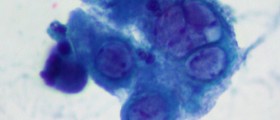
Doctors usually recognize herpes symptoms in patients, but in order to prescribe antiviral medications, patients must be diagnosed and confirmed by some lab testing. HSV infection can’t be cured and there is no known cure for it. Once infected, person remains infected for life, and the virus stays for good in the body.
Microbiological proof is necessary to confirm the diagnosis, as we already said, and after that doctors are able to prescribe appropriate treatment. HSV diagnostic methods include: isolation of viruses, direct detection of viral antigens (immunofluorescence on the culture of cells), PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and type-specific serology (which include Western blot, ELISA tests and enzyme immunoassay). The golden standard in serological testing on HSV antibodies is Western blot test.
Antiviral drugs are prescribed to ease the symptom and decrease the rate of viral shedding and viral transmission to sexual partners.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...