
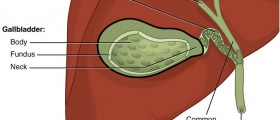
GallbladderGallbladder is a tiny organ that lies under the liver on the right side of the upper abdomen. Gallbladder is a reservoir which stores bile. When we eat, gallbladder contracts thus empty stored bile which goes to duodenum and helps in digesting food.
Causes of Inflamed Gallbladder
Commonly, gallbladder inflammation is caused by gallstones. Gallstones get stuck in the cystic duct which leads to accumulation of bile inside the gallbladder which becomes stretched. This results in inflammation and infection of gallbladder. This causes acute inflammation of the gallbladder in 90% of the cases.
In chronic cholecystitis, the gallbladder is damaged by repeated attacks of acute inflammation, usually due to gallstones, and may become thick-walled, scared and small.
Sometimes, a tumor can cause development of the gallbladder inflammation.
Symptoms of Inflamed Gallbladder
One of the first symptoms, that people affected by inflamed gallbladder experience, is abdominal pain on the right side of the body. This pain can be severe and last for several hours. It is usually triggered by greasy food. Chest pain and heartburn are also associated with inflamed gallbladder. Chills are another symptom, usually accompanied by shaking and sweating. Other symptoms of cholecystitis include: indigestion, fever, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin).
Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder involves symptoms such as sporadic abdominal pain, nausea, belching and chronic diarrhea. Occasionally, chronic cholecystitis isn’t followed by any symptom.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Inflamed GallbladderAn ultrasound is commonly done to confirm the diagnosis. Apart from that, doctor must perform physical examination and inquire about the symptoms. Other tests that are necessary to clarify the diagnosis are: blood count test, levels of the enzymes, amylase and lipase in the blood, level of bilirubin, and liver function test.
A patient is normally admitted to hospital and isn’t allowed to eat or drink. Patient receives IV fluids and painkillers. When inflammation and symptoms settle down, a doctor may recommend a special diet low in fat. In case of infection, patient will receive antibiotics by intravenous route. Some patients also receive medications for nausea and vomiting. In severe cases of inflammation, surgery must be performed to remove the gallbladder.
Untreated cholecystitis can result in serious complications.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...