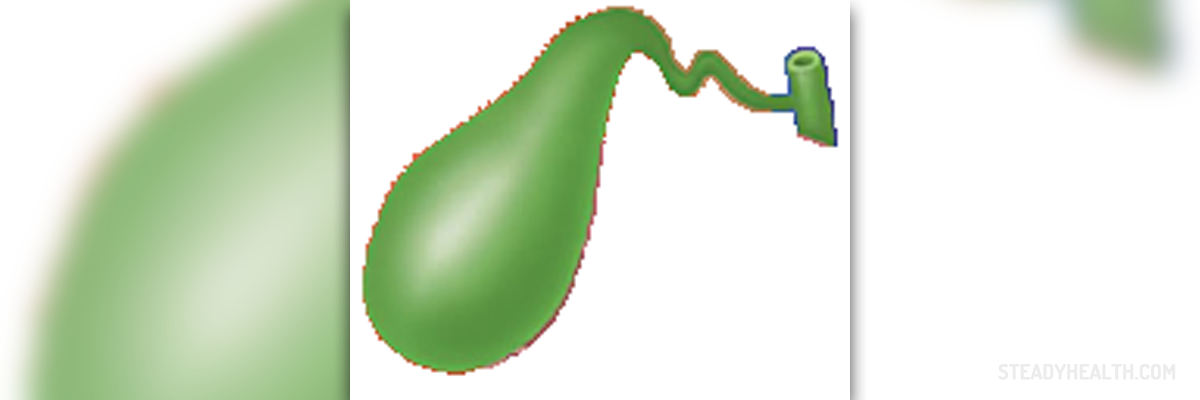
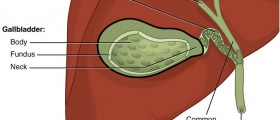
The gallbladder is a small organ situated in the abdomen. Its precise location is below the liver. The gallbladder is connected with the liver by the hepatic duct. This way the excess of bile synthesized by the liver can be stored in the gallbladder and used if there is a need for that.
GallstonesGallstones are solid formations that form inside the gallbladder. There may be one or more gallstones in the gallbladder. These formations develop due to high level of cholesterol. The excess of cholesterol leads to its crystallization and formation of gallstones. Even though the excess of cholesterol represents the major cause of gallstones formation these solid formations may also develop due to deposits of calcium and bile pigments.
Gallstones seem to be hereditary and run in families. This is why positive family history of gallstones carries a significant risk of their formation in healthy people. Gallstones are also associated with obesity, consumption of too much of fatty foods and heavy drinking. The risk is also increased in women over the age of 40 who have many children.
CholecystitisThe major cause of cholecystitis is the presence of gallstones. They cause inflammation of gallbladder and are responsible for many unpleasant symptoms of the condition and may also cause severely serious complications. Cholecystitis features with the pain under the right rib cage that commonly radiates towards the shoulder blade, nausea, vomiting, bloating etc. The stone may only irritate the gallbladder and cause its inflammation or in severe cases it may leave the gallbladder and cause obstruction of the hepatic duct. What is more in case the inflammation of the wall of the gallbladder becomes severe and the tissues of the wall become necrotic there is increased risk of perforation and one on the most serious complications of cholecystitis- inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis).
Treatment for CholecystitisCholecystitis is initially treated conservatively and once the inflammation subsides patients undergo gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy).
Conservative treatment includes intake of fluids (either orally or intravenously), cease in food intake, bed rest and antibiotics. Painkiller and spasmolytics take care of the pain caused by inflammation.
In patients who are suffering from serious complications such as perforation of gallbladder or obstruction of bile ducts the surgery must be performed straight away. These are life-threatening complications and they cannot wait for the inflammation to subside. Only if a patient is suffering from an inflammation of gallbladder without additional complications doctors wait for the inflammation to go away and then perform cholecystectomy.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...