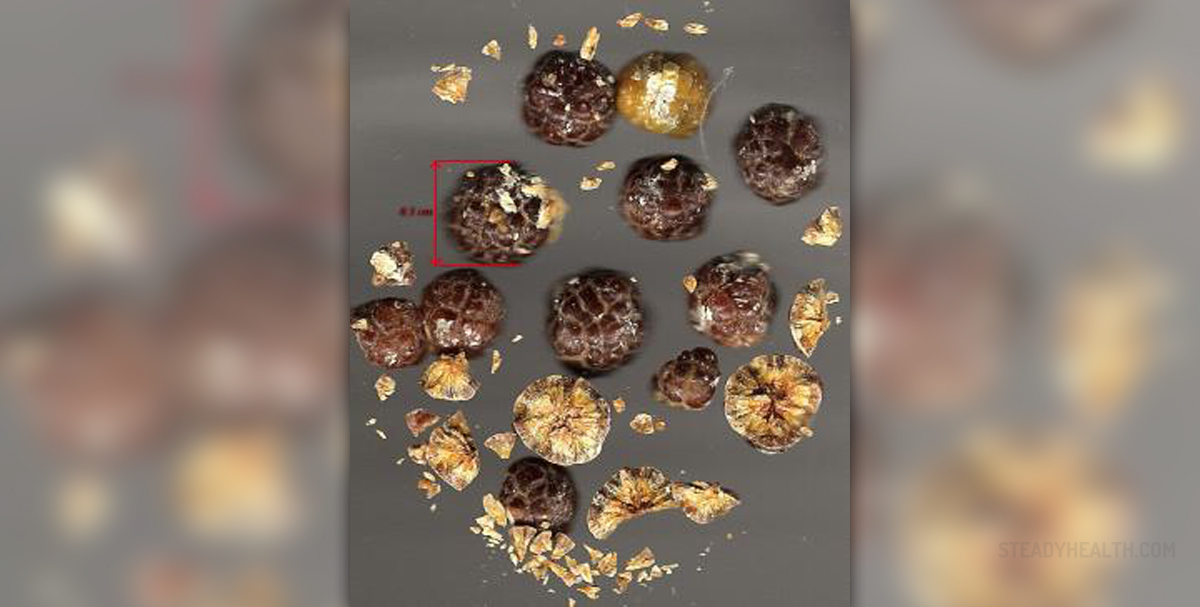

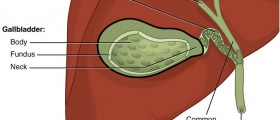
Gallstones are crystalline concretions formed within the gallbladder by accretion of bile components. These calculi, or stones, form in an organ or duct of the body. Gallstones are actually hardened deposits of digestive fluids. The formation of calculi is known as lithiasis. Gallstones are formed in the gallbladder, but they may pass into other parts of the biliary tract: the cystic duct, common bile duct, pancreatic duct, or the ampulla of Vater. Gallbladder is a small organ that aids digestion and stores the bile produced by the liver. The gallstones in the gallbladder may cause the acute cholecystitis. This condition is also known as a gallbladder attack or an inflammation of the gallbladder.
Causes of gallstones
It is not completely clear what causes gallstones. Scientists believe that people near or above age of 40, pre-menstrual women and overweight population, are at an increased risk. For some reason, gallstones are more common in caucasians, than in people of other races. Gallstones are probably caused by the combination of numerous factors such as body chemistry, weight, gallbladder movement and diet. Doctors believe that gallstones may result if one's bile contains too much cholesterol. This cholesterol may gradually form into crystals and stones. What is important to understand is that cholesterol in the bile has nothing to do with cholesterol in the blood.
If bile contains too many bilirubin, a chemical that is produced when the body breaks down the red blood cells, gallstones may form. Gallbladder contractions are responsible for the emptying of the gallbladder. If the gallbladder does not empty correctly, bile may become very concentrated and form gallstones.
Symptoms of gallstones
For many patients, gallstones are asymptomatic for a number of years. These asymptomatic gallstones are usually called “silent stones", and they do not require any kind of medical treatment. Treatment becomes necessary when the stone reaches a size larger than 8mm in diameter. The person may feel intense pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, where the gallbladder is located. Patient may feel nausea and an urge to vomit. The attack may last anywhere from 30 minutes to a couple of hours. Some patients report pain under the right arm. By rule, attacks occur during the night and commonly after a fatty meal. Sometimes, the pain is sudden and rapid, and it radiates from the center of the abdomen, just below the breastbone. The patient may also feel pain between the shoulder blades.
A patient should consult a medical care provider if the abdominal pain is extremely intense, if there is yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, or if the symptoms are accompanied with chills and fever.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...