Gallbladder and Children
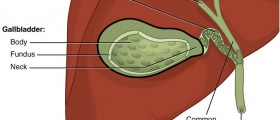
One of the organs of the digestive tract is gallbladder, it is situated under the liver and has the role to store the bile and squeeze it into the intestines. It is very important to keep it healthy, but the fact is that because of various causes certain gallbladder disorders may occur. Earlier, the gallbladder disorders were very rare in children. Nevertheless, in recent years the number of children with gallbladder problems increased significantly.
One of the main gallbladder disorders is the appearance of gallstones, which can cause sharp pain when they block the bile ducts. These ducts have the role to transport the bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine, but when these ducts are blocked, gallbladder becomes inflamed. Cholecystitis is the medical term for the infection or inflammation of the gallbladder. It can be mild and not very serious, or chronic, which is serious. Acute gallbladder infection is caused by a virus or bacteria and usually affects the younger children. In this case, the gallbladder becomes full of liquid and its walls become thicker. Sometimes acalculous cholecystitis may occur as well, and it is a kind of acute cholecystitis when the gallstones are not formed in the gallbladder. On the other hand, chronic gallbladder infection lasts for a long period of time and is characterized by the forming of gallstones in the gallbladder.
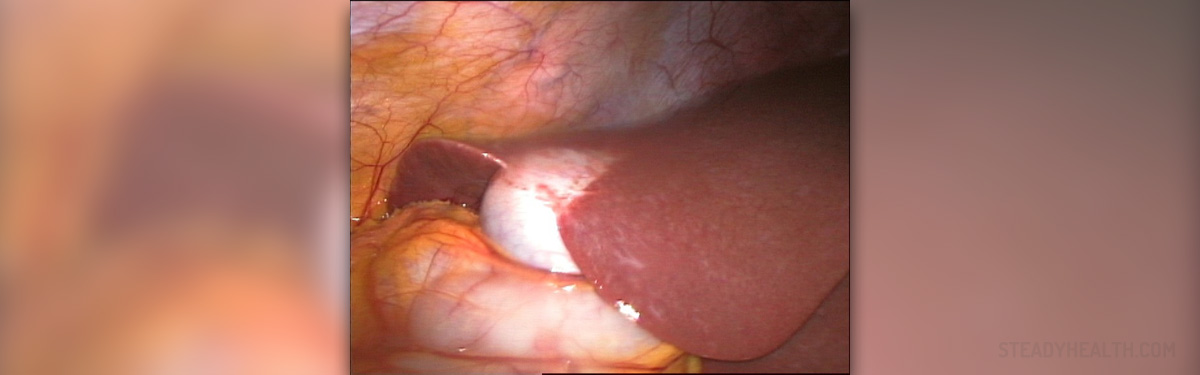
Chronic cholecystitis usually occurs in children between 11 and 20 years of age. The gallstones in children are usually black pigment, cholesterol, calcium carbonate, protein dominant, or brown pigment stones.
- Indications for cholecystectomy were gallstones in 285 (63%) and biliary dyskinesia in 140 (33%).
- Of the patients with gallstones, 68 children (15%) had hemolytic disease. Although the number of cholecystectomies for hemolytic disease was relatively stable throughout our study, the number for biliary dyskinesia and non-hemolytic (cholesterol) cholelithiasis rose by 63% and 216%, respectively.
- Average body mass index (BMI) for patients with non-hemolytic (cholesterol) stones and biliary dyskinesia were significantly greater than the average BMI for patients with hemolytic stones (P
Causes of Gallbladder Problems in Children
The most common causes of gallbladder disorders in children are weak immune system, obesity, previous abdominal surgery, injury, and long parenteral nutrition. Other causes of gallbladder problems include low calorie diet, acute renal failure and certain medications, as well as liver diseases.
Symptoms of Gallbladder in Children
In the majority of cases, the gallbladder symptoms in children appear suddenly and are misdiagnosed as the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. The most frequent symptom of this condition is the sharp pain that occurs in the upper abdomen on the right side. This pain may even last 12 hours, but it is also possible that the pain may spread to the back and between the shoulder blades. High body temperature, fever and chills are also common symptoms of the gallbladder inflammation in children. The children with gallbladder problems may also experience nausea, vomiting, gas and bloating, as well as indigestion and burping.
When the symptoms mentioned above are persistent, it is very important to take the child to the doctor who will prescribe a proper treatment if the presence of gallstones is established.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...