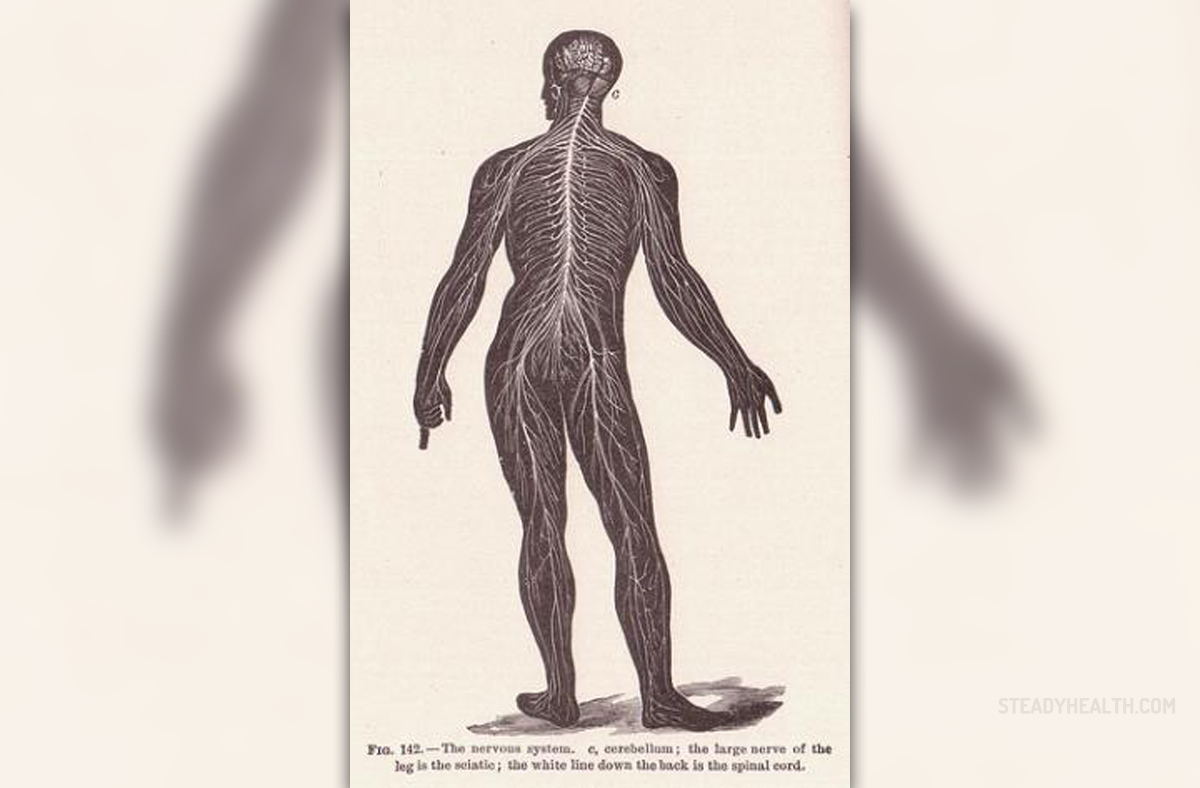
HowAlcohol Affects the Human Nervous System
Alcoholhas a very particular effect on humans, typically causing lack ofcoordination, loss of motor function and desensitisation, amongothers. This happens because alcohol blocks electric signals thattravel along the nervous system between the nerve endings, spine andbrain. Alcohol enters the bloodstream when consumed and slowly beings to affect thenervous system.
Thehuman body consists primarily of two different systems: the voluntary(those bodily functions which one can control) and the involuntary(those functions that one cannot control). The involuntary systemincludes breathing and the heartbeat. Excessive alcohol consumptioncan impair or shut down these systems and can prove fatal.
Alcoholis created by the fermentation of grains, as well as fruits andhoney. Sugar within these foodstuffs is turned into alcohol with theuse of yeast. Alcohol has many uses, from cleaning to medicine, butits most common use is in beverages for human consumption. Consumingsmall amounts of alcohol gives a person a 'buzz', while largeramounts cause inebriation and eventually hangovers (which is thebody's reaction to minor alcohol poisoning). Drinking in largequantities too often can cause severe health issues affecting theliver, pancreas, mouth, heart, bloodstream, bones and peripheraltissues in various ways, and can even lead to the development ofpsychoses. These effects will be different according to theindividual's alcohol tolerance, as well as other health problems.
LongTerm Effects of Alcohol Consumption
As aperson builds up a tolerance to alcohol, their cells change to absorbless alcohol, technically becoming thicker. A thick walled cell is anunhealthy one that weakens the body's immune system. This can lead toproblems such as stroke, heart attack and dementia, as well as otherdiseases and infections that will take advantage of a poor immunesystem defence.
Regularconsumption of large amounts of alcohol can also lead to anaddiction, which has the same typical symptoms as many otheraddictions, including nausea, panic, tremors, sleep disorders,anxiety and perhaps even hallucinations. Excessive drinking alsodamages the brain, reducing the size of the frontal lobes.
Vitamindeficiency is another problem incurred by alcohol addiction, causedby the digestive system not being able to absorb thiamine. This leads to symptoms such as short-term memory loss,impaired vision, confusion and lack of coordination.
Dependingon the gender, physical state and age of a person, alcohol willaffect them in different ways. Also, if alcohol is taken with anotherdrug, it may lead to terrible consequences due to the bloodstreambeing poisoned. Minor alcohol consumption will typically relax aperson, slow down the reflexes and impair the coordination to asmall degree. Moderate consumption will mean a fair amount ofdrowsiness, impaired speech and wide-ranging mood swings. Majoralcohol consumption will cause breathing problems or even outrightfailure, panic and unconsciousness that can occasionally even lead tocoma. Alcoholism leads to depression, anxiety and various forms ofpsychosis.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...