The heart is a vital organ, necessary for survival since it supplies the body with the required nutrients and oxygen. It is essential to maintain a healthy heart because any disorder or disease that affects the heart can further damage the other parts of the human body.
Just like every organ in the body, the human heart can develop a disease or can be affected by some disorders. One of the hearts problems is a heart attack, which occurs when the heart does not get enough oxygenated blood due to certain blockage in the coronary arteries. The main symptoms of a heart attack are chest pain or angina, breathing problems, and faintness.
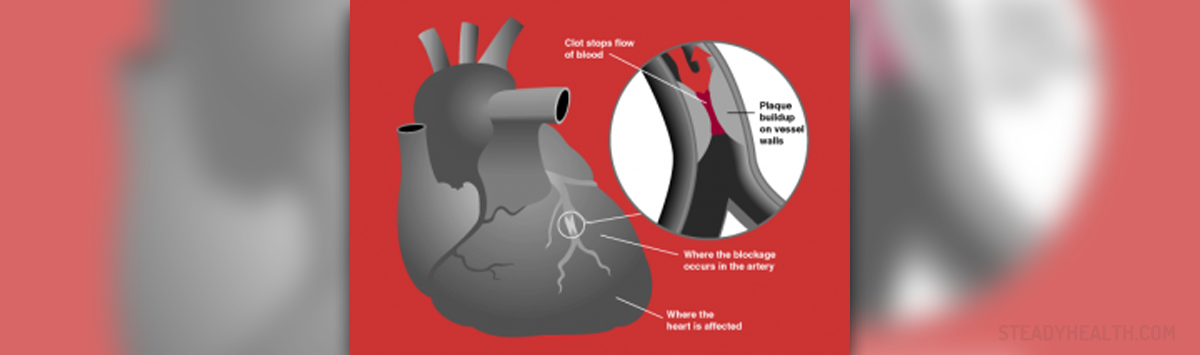
Causes of Heart Attack
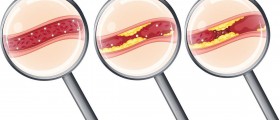
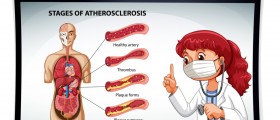
Blocked arteries are a major cause of heart attacks. These arteries become blocked or narrowed due to the buildup of cholesterol, calcium, and fatty material on the walls of the arteries. This accumulated material is actually plaque. The medical term for the forming of plaque is atherosclerosis, which is actually a very slow process that can take decades to develop.
Certain conditions may aggravate atherosclerosis and among them are hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol levels, and the use of alcohol and cigarettes. Apart from the blockage of the coronary arteries, another cause responsible for the occurrence of a heart attack is the spasm of the coronary artery. This condition may be induced by excessive smoking, use of narcotics, or constant stress.
How Does a Heart Attack Affect the Body?
It is quite normal that any disease or disorder within the body affects some organ, system, or the overall health of the person. Thus, heart attack also has several negative effects since the heart is responsible for blood circulation throughout the body. One of the consequences of a heart attack is arrhythmia, which is an irregular heartbeat rhythm. This problem is likely to make the heart weaker over time and can be a life-threatening condition.
Furthermore, heart valves may be considerably affected by a heart attack. Because of that, leakage of the blood may occur, which is also a very serious condition. When the muscles of the left ventricles are impaired in a heart attack, the heart is not capable of effectively pumping the blood, which leads to the occurrence of congestive heart failure. The heart attack may also provoke myocardial rupture. This is actually a tear in the heart muscle that can lead to excessive bleeding, which is why myocardial rupture is considered to be a very serious heart disorder.
- Over a period of 1,079,044 person-years (median 2.2 years of follow-up), 113,586 (29.2%) NSTEMI patients died. Of those eligible to receive care, 337,881 (86.9%) did not receive one or more guideline-indicated intervention; the most frequently missed were dietary advice (n?=?254,869, 68.1%), smoking cessation advice (n?=?245,357, 87.9%), P2Y12 inhibitors (n?=?192,906, 66.3%) and coronary angiography (n?=?161,853, 43.4%).
- Missed interventions with the strongest impact on reduced survival were coronary angiography (time ratio: 0.18, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.17–0.18), cardiac rehabilitation (time ratio: 0.49, 95% CI: 0.48–0.50), smoking cessation advice (time ratio: 0.53, 95% CI: 0.51–0.57) and statins (time ratio: 0.56, 95% CI: 0.55–0.58).
- If all eligible patients in the study had received optimal care at the time of guideline publication, then 32,765 (28.9%) deaths (95% CI: 30,531–33,509) may have been prevented.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...