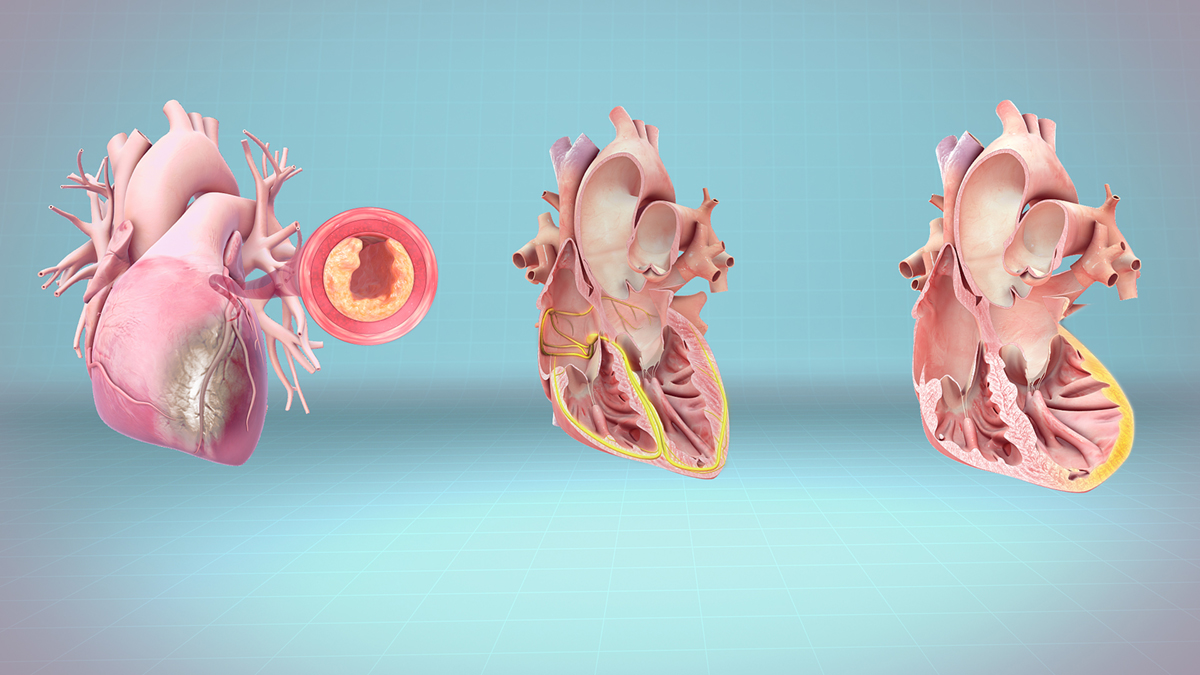
Heart attack-Overview
Also called myocardial infarctation, a heart attack usually occurs when a blood clot blocks the flow of blood through a coronary artery (a blood vessel that feeds blood to a part of the heart muscle). Interrupted blood flow to the heart can damage or destroy a part of the heart muscle. A heart attack was often fatal. Thanks to better awareness of heart attack signs and symptoms and improved treatments, most people who have a heart attack now survive. And there are sure ways of decreasing one’s risk of getting a heart attack and they include: regular exercise, avoiding smoking and alcohol, eating fresh fruit and vegetables, and reducingstress.
There are many things that can cause a heart attack, most common being a blockage of the arteries. Also, it can be induced by atherosclerosis, or, less commonly, a spasm of the coronary artery.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms that a person is having a heart attack are: a pressure or discomfort in the chest, arm, or below the breastbone, choking feeling (may even be described as heartburn), weakness, shortness of breath, anxiety, rapid or irregular heartbeats, nausea, sweating, dizziness, etc.
During a heart attack, symptoms last 30 minutes or longer and are not relieved by rest or nitroglycerin under the tongue. Also, some people may have a heart attack without actually experiencing any symptoms (a "silent" myocardial infarction). A silent MI can occur in any person, though it is more common among diabetics.
Heart attack inwomen
Many women feel that heart attack is not the greatest risk they might face. However, they should know that the risk of a women getting a heart attack increase significantly around menopause, because hormonal changes may open the door for many diseases, among which cardiovascular disease. And it has been reported that every year hundreds of thousands of women die as the result of a heart attack or other cardiovascular disease.
When it comes to women, heart attack warnings can be subtle, and early symptoms of cardiac distress can even emerge days or even weeks before the actual heart attack. However, being that they are considered to be usual for menopausal women, they often go unnoticed. The early symptoms of heart attack in women are sleep disturbances and fatigue. A recent study conducted has shown that almost 70 per cent of women have stated that they have experienced fatigue and sleep disturbances weeks prior to the attack.
If one notices these symptoms, it is always advisable that they consult a doctor, especially if they have increased risk of getting a heart attack (i.e. if they have high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity; if they smoke, etc). Research shows that women frequently ignore signs of illness or attribute their symptoms of cardiac distress to something else. This should not be done, but, at any sign of trouble, a doctor should be consulted. In that way, many unnecessary problems will be averted.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...