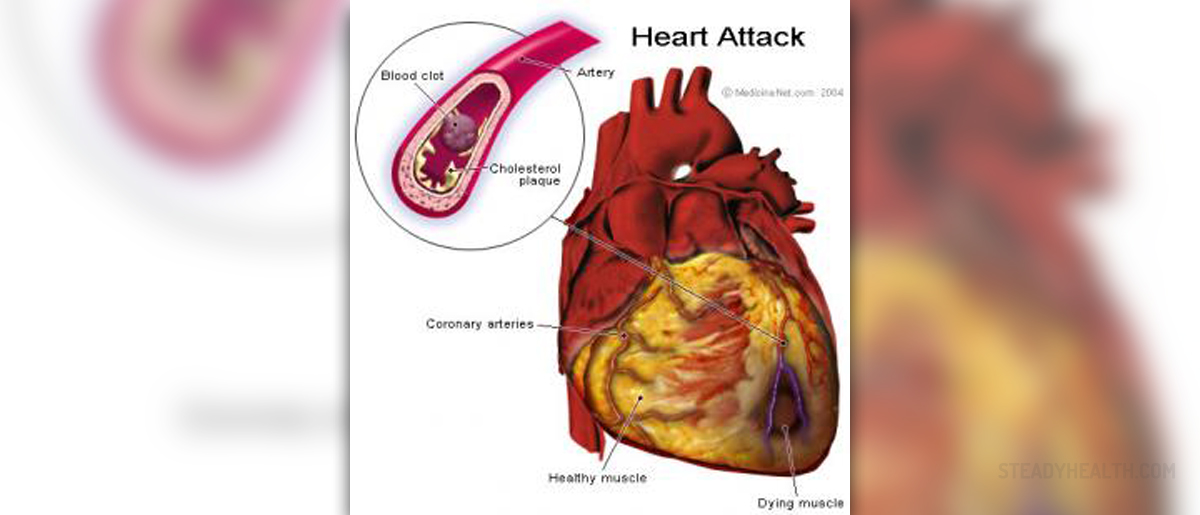
Heart Attack
Many patients die from a heart attack just because they do not recognize the first signs of disease and they ignore the possibilities and meaning of urgent treatment.A heart attack is caused by sudden interruption of blood flow in the arteries that bring blood to the heart muscle, resulting in the withering away the limited part of muscular heart wall.
The most common direct cause of heart attack is a thrombosis - blockage of blood vessels by the blood clot. Today, the high percentage of blood clots may be dissolved by drugs, restoring the blood vessels flow in the myocardium. However, this treatment can be applied only when the patient arrives in the hospital on time.
Initial Symptoms of Heart Attack
There are many and various signs by which a heart attack is announced. Some of them are very rare while some are similar to signs of other diseases, such as indigestion.The most common and most important symptom is a pain. Patients describe the pain as pressure, weight, squeezing and crushing beneath the sternum. Pain is not strictly limited and patients generally cannot point the place of the strongest pain. Pain can take hours, usually doesn’t take less than half an hour.
The pain may spread to other parts of the body, usually to the left shoulder and arm, rarely to both or only to the right shoulder. It can be felt in the neck, jaw, sometimes in the upper abdomen and the epigastrium.
Pain is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, paleness and dewy skin with a cold sweat. Patients feel fear from immediate death.
About 60% of patients have experienced a heart attack in a completely idle state, often in a dream.
Silent Heart Attack
Heart attack is usually associated with the dramatic scenes from the movies: a person is holding the chest, cannot breathe and crashes to the floor in pain. There are greater chances for heart attack with no real symptoms.Undiagnosed silent heart attacks are affecting almost 200,000 Americans a year. Data show that people overcome between 40 and 60 percent of all heart attacks without knowing it. Risk factors for silent heart attack are the same as for "classic", including smoking, stress, family history of disease or diabetes. If a person had heart attack in the past, doctors can see that through the signature in Q-waves on ECG. The problem is that every heart attack does not leave such a signature.
Scientists have used a new process of imaging the heart by slow high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging to detect the damage caused by previous infarcts. The procedure has involved 185 persons in whom heart attack has never been diagnosed, but they were believed to suffer from cardiovascular disease.
They found that 35 % of examined persons had heart attack. A silent heart attack without the Q-wave signature was three times more common than one with such a signature.
Treatment of the person who had silent heart attack should be the same as that in patients who was hospitalized immediately after the attack.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...