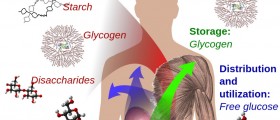
The focus of this text will be cast on the important matter of glucose level in children. It is important to maintain a normal level of glucose through proper nutrition regime and exercising. This may be a bit more challenging, especially if we know that daily activities of a child today change very frequently. It may be a problem to implement one plan for the glucose level monitoring. This level is shown in the milligrams per deciliters and it shows how much cells are produced by your body. The level of glucose in the body is maintained by the two hormones called glucagon and insulin. They are created by an organ named pancreas, which is a part of the digestive system. When there is a need for the simple sugar, or glucose, the release of glucose is done by the insulin, which is administered into the bloodstream. Insulin administers the glucose into the cells. Next, the cells produce energy from the glucose located in the liver and muscle cells where they are located in the form of glycogen. When the glucose is used as an energy source, like when we exercise, the glucagon used the glucose for this purpose. The manufacture of glucagon in these situations is increased and the insulin manufacture is reduced by the pancreas. The glucose, or glycogen, in the liver is broken down by the glucagon, which leads to the normalization of the level of production of glucagon, by the administration of glucose to the bloodstream.
Normal Glucose Level in Children
Now we will see which figures show normal glucose level in children of various age. Blood sugar from 100 to 200 mg/dL is normal for children below five years. Prior and after the meal (two hours exactly) the level should be maintained. The normal range before going to bed, for this age, goes around 150 mg/dL. This level is a bit lower, 120 mg/dL for children from five to eleven. Maintenance of the level can be done in the same periods of time, but during the day, the children of this age group should have from 70 to mg/dL. Children older than twelve should have blood sugar ranging from 70 to mg/dL during the day and 100 mg/dL prior to the bedtime.
High glucose Level
When children are not exercising or are not involved in the physical activities, or when they are under stress, the insulin is produced in increased amounts and this causes increased glucose. The blood sugar is considered high if it ranges from 200 to 350 mg/dL. Dry skin, drowsiness, dehydration and frequent urination are symptoms of high blood sugar. Diabetes mellitus, diabetic coma and blurred vision can occur if the glucose level reaches 350 mg/dL. This problem is called hyperglycemia. The opposite of this is the problem called hypoglycemia. Glucose level from 55 to 70 mg/dL is considered low. Fuzzy thinking, dizziness, palpitations, weakness, and hunger are problems experienced by this condition. Eating more is advised in these situations. It is also a good idea to monitor the level of glucose in your children regularly. For this you can use a monitoring kit, but be sure to follow the instructions.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...