Human brain and other cells in the body need glucose (blood sugar) to function. Endocrine system is responsible for the control of blood sugar, so it determines whether glucose is going to be used as energy fuel or stored in the cell.
Who Need to Test Blood Glucose?
Diabetes mellitus patients need to closely watch the level of their blood sugar. Usually, these patients have to perform these tests several times a day, in order to see how high or low their glucose is. After the test, they can adjust their medications or insulin, according to the results.
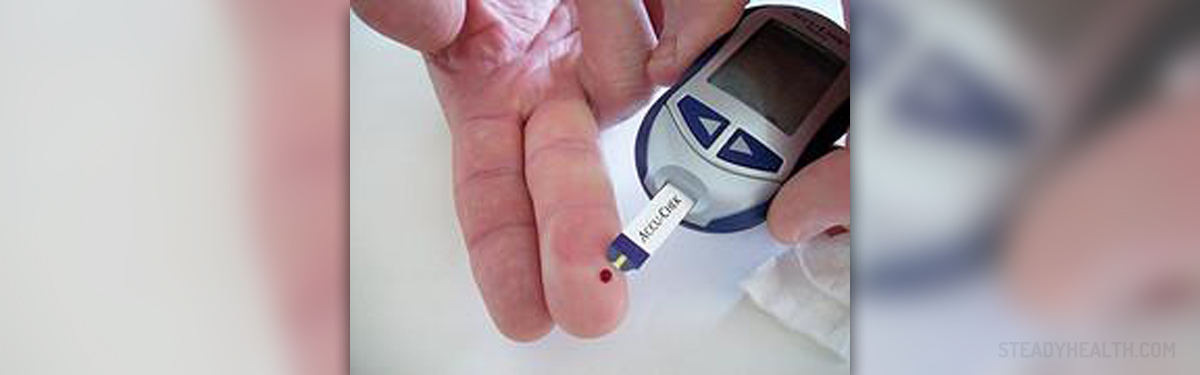
All these patients need is a drop of their blood from a finger. Then, they place that drop on the so-called glucose strip and that strip goes into blood sugar tester. This small device provides digital read of the level of blood sugar in that blood sample and a patient knows what medication he or she needs.
Beside this home test, laboratories also perform glucose tests. Labs commonly use blood samples, but in some cases they could also take urine and determine the amount of glucose in that sample. Blood glucose test may be used to diagnose or to monitor diabetes.
Blood Sugar Tests
There are several types of blood glucose tests that could be performed in laboratories. Usually a laboratory technician takes a sample of your blood and you have results of your blood sugar just several minutes after that. Diabetics may also have heightened level of glucose in urine, if their blood glucose level is extremely high. Since this is rarely the case, urine samples are not useful in diagnosing or monitoring someone’s diabetes.
Fasting blood sugar test (FBS) is used to measure amount of glucose in the blood 8 hours after the person ate something. This is usually one of the first tests to diagnose diabetes. Healthy people normally have less than 100mg of glucose in 1dl of blood sample (100mg/dl). Pre-diabetes condition is characterized by 100 to 125mg/dl of glucose in the blood, while diabetics have more than 126mg/dl of blood sugar.
Random blood sugar test (RBS) may also be used to diagnose diabetes. It measures level of glucose in the blood in any particular moment. Pre-diabetes patients have about 140 to 200mg/dl of glucose. To confirm someone’s suffering from diabetes, that person should have more than 200mg/dl in RBS test.
To diagnose diabetes in pregnancy doctors and laboratories use oral glucose tolerance test. According to this test, a woman doesn’t have blood sugar problems if there are less than 140mg/dl of glucose in her blood. Pre-diabetes is diagnosed in women with 140 to 199mg/dl of glucose in the blood.
Glycated hemoglobin test (A1C) is useful for monitoring of diabetes management, showing percents of hemoglobin which has become glycated (covered with sugar). For healthy people, it is normal to have about 4 to 6% of glycated hemoglobin and diabetics should maintain about 7% of glycated hemoglobin.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...