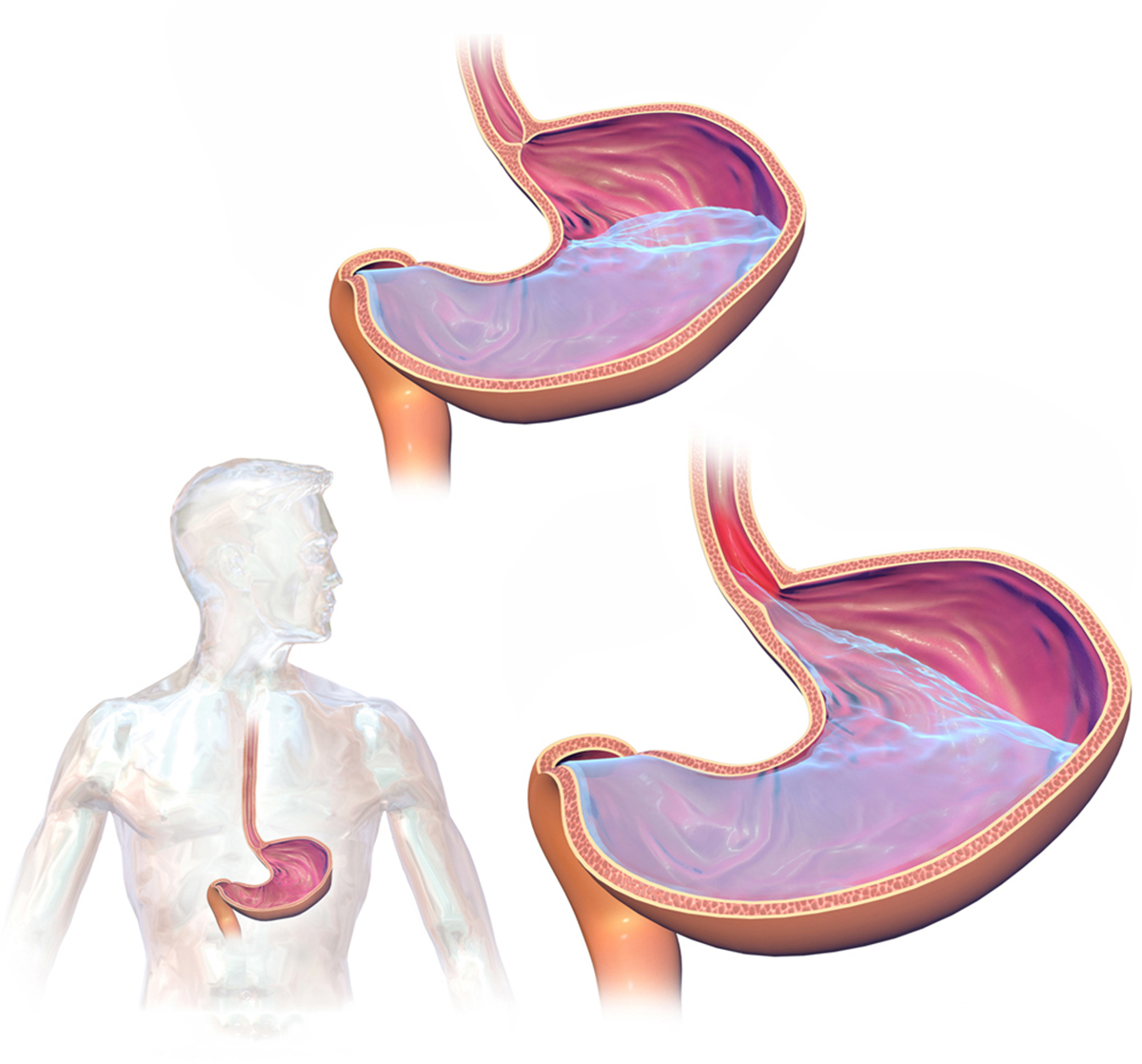
Introduction
There are different treatment modalities for gastroesophageal reflux disease. The surgery is the last option in all those who do not react to life style changes and medical therapy. The goal of the surgery is to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and prevents possible complications such as Barrett's esophagus, esophageal strictures or esophageal ulcers. Patients who are chosen for the operation have to be examined thoroughly. The acidity in the esophagus is monitored within a period of twenty-four hours. This way apart from obvious and evident symptoms of increased acidity even the asymptomatic hyperacidity in the esophagus can be noticed. There is one more study which is conducted to determine whether the patient is suitable for operation. It is called esophageal manometry. Esophageal manometry measures the coordination of esophageal muscles and their functioning. And finally before the very surgical procedure one is subjected to endoscopy. This way the surgeon can actually see the possible changes on mucous membrane.
Laparoscopic Surgery for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
This minimally invasive procedure is most frequently performed in case of this disease. In this surgical procedure the small incisions are made and the surgeon performs the operation with the assistance of the camera. It is suitable as the patient can continue with the regular activities rather soon after the surgery. There is slight chance of complications in laparoscopic approach.
The heartburn is relieved in approximately 90% of all operated patients and 85% of patients do not suffer from respiratory problems any more. The procedure is effective as it results in prevention of the reflux of both, stomach acid and bile. Bile regurgitation is connected to the occurrence of the esophageal cancer. Therefore the surgical treatment is perfect prevention against this type of cancer. Minor post-surgical problems may be connected to accelerated stomach emptying.
The surgery is perfect therapeutic method for all those who are doomed to medications for life and for those who are suffering from respiratory complications of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Complications of the Surgery
The postponing of the intestinal recovery usually leads to vomiting and flatulence. These problems tend to fade away in several weeks. Additional complications include intestinal obstruction and the infection of the operated area. Even the surrounding organs can be damaged during the procedure. Some patients even develop respiratory complications. If the fundus or the upper part of the stomach is wrapped a patient may complain about problems with swallowing. In case that esophageal muscles become spastic the act of swallowing is followed by intensive pain. Additional operation is necessary if the surgically placed wrap is not tight enough or if it has slipped or if the problems with swallowing do not withdraw. The repeated surgery is even performed in case of development of hernia or recurrent ulcers.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...