Gastroesophageal reflux disease also known as acid reflux disease is a chronic medical condition that leads to serious damage due to regurgitation of the stomach acid into the esophagus. The most typical symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease is heartburn.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease usually develops as a consequence of changes in the barrier between the stomach and the esophagus. The most common cause is improper and abnormal relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter. This muscle normally holds the top of the stomach closed and in case of its insufficiency the acid is free to enter the esophagus and cause all the damaging effects.
Clinical Characteristics of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
The most common symptoms in adults are heartburn, the feeling of acid regurgitation and troubles swallowing. Pain during swallowing as well as excessive salivation are two more not so frequent symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Some people may additionally complain about nausea and chest pain.
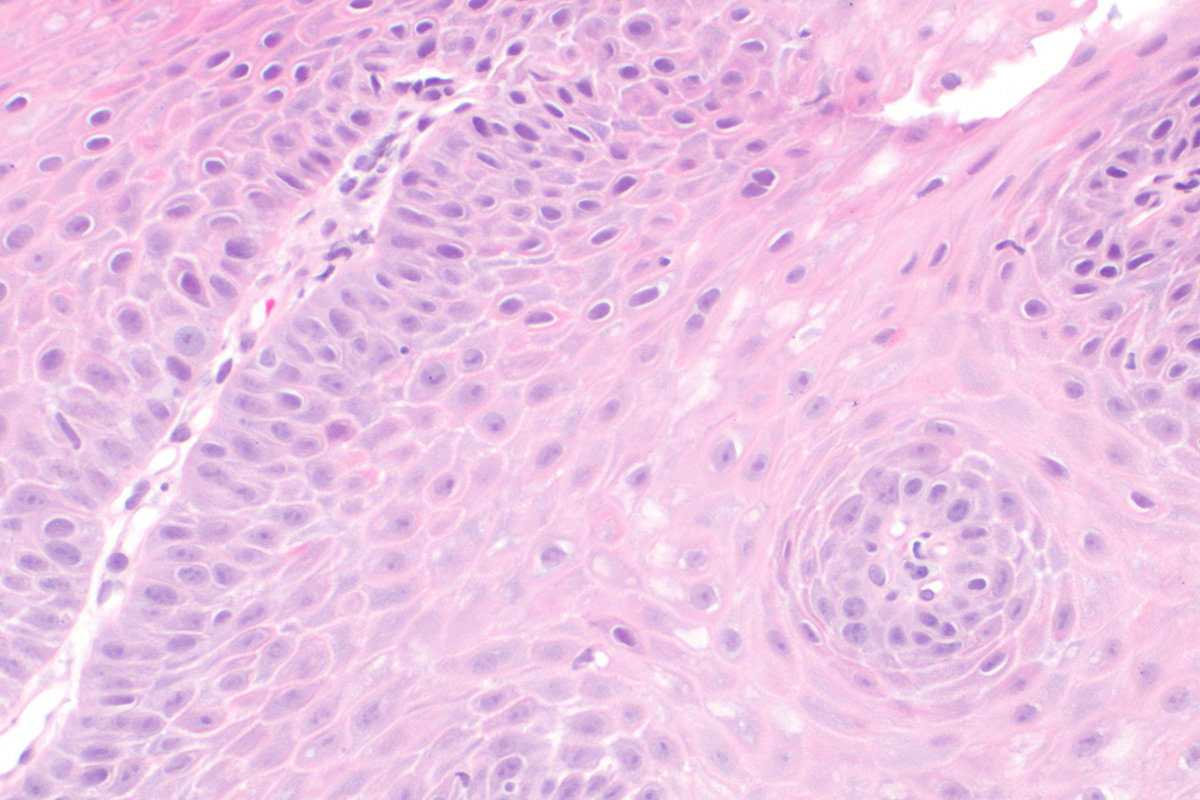
In patients suffering from gastroesophageal reflux disease prolonged irritation of the esophagus with the stomach acid eventually leads to necrosis of the esophageal epithelium and formation of esophageal ulcer, esophageal strictures (narrowing of the esophagus), Barrett's esophagus (changes of the epithelial cells from squamous to intestinal columnar epithelium) and esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Chronic irritation caused by stomach acid may also lead to chronic cough, laryngitis, asthma, erosion of dental enamel, dentine hypersensitivity, sinusitis and damaged teeth.
Diagnosing Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
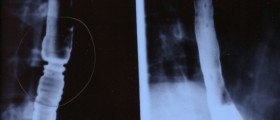
The first step in diagnosing gastroesophageal reflux disease is thorough investigation of patient's medical history. Additional information is obtained with barium swallow X-rays, esophageal manometry, endoscopic image of the esophagus and the stomach.
Currently the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease is based on esophageal pH monitoring. This is considered the most objective test for diagnosing gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Biopsy of the esophageal tissue may point to structural changes such as edema, basal hyperplasia, intestinal metaplasia and even dysplasia and cancer cells.
Treatment for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
The first thing patients must do is to make lifestyle changes. They are supposed to avoid certain foods, lose weight and keep the head elevated while sleeping since only this way the regurgitation of the stomach acid can be successfully controlled. Smokers must quit smoking and those who are prone to alcohol must abstain from consumption of alcohol beverages.
Medications commonly prescribed for gastroesophageal reflux disease include proton pump inhibitors, gastric H2 receptor blockers and antacids. Procinetics are effective when it comes to strengthening the lower esophageal muscle and are able to speed up emptying of the stomach.
The last option for patients suffering from gastroesophageal reflux disease is surgery. The Nissen fundoplasty is a standard surgical procedure performed in such patients. It includes strengthening of the lower esophageal muscle and is in majority of cases performed laparoscopically.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...