Any disease is more likely to have a better outcome if the problem is diagnosed in its early stages. This rule can also be applied to cancerous changes in the body, including esophageal cancer. Noticing first symptoms and reporting them to your doctor is extremely important so that you can receive proper diagnosis and treatment, avoiding unnecessary complications.
You have to watch your body and notice problems as they arise. Consulting your doctor about potential problems may lead to an early diagnosis and a good prognosis of esophageal cancer.
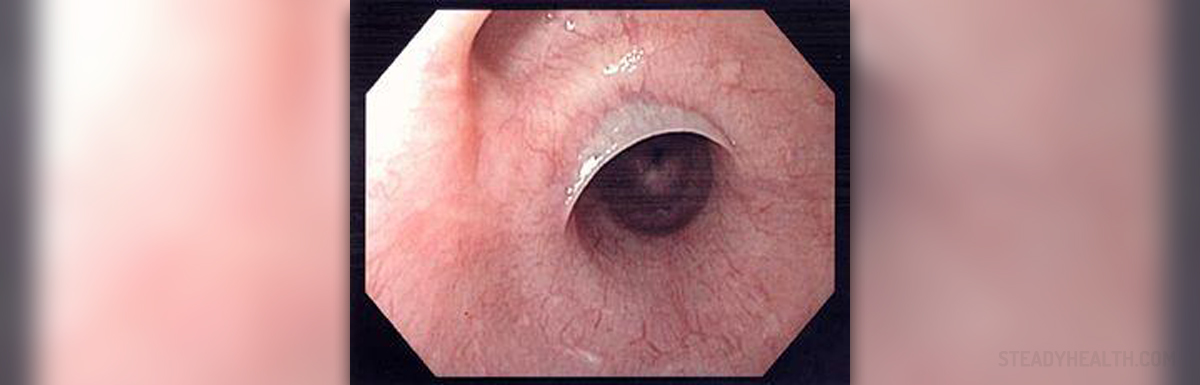
First Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
In some cases, patients are not able to tell that anything is wrong with their bodies. This happens because esophageal cancer is known not to cause any problem or sign in the early stages of development in most patients. Other patients experience swallowing problems and feel as if the food has stuck in their throat for some time after eating.
Sudden, unwanted, and unexplained loss of appetite and weight loss may also suggest that the person has esophageal cancer and this sign is also very common. Some people may experience pressure and pain in the throat or in the chest, all because of the growth of esophageal cancer. If the tumor affects the movement of food from the esophagus to the stomach, the patient may feel discomfort and pain while eating something, but this is more likely to happen in advanced stages when the tumor becomes fairly big.
- The most common symptom of esophageal cancer is a problem swallowing (called dysphagia). It can feel like the food is stuck in the throat or chest, and can even cause someone to choke on their food. This is often mild when it starts and then gets worse over time as cancer grows and the opening inside the esophagus gets smaller.
- Sometimes, people have pain or discomfort in the middle part of their chest. Some people get a feeling of pressure or burning in the chest. These symptoms are more often caused by problems other than cancer, such as heartburn, so they are rarely seen as a signal that a person might have cancer.
- Many people with esophageal cancer lose weight without trying to. This happens because their swallowing problems keep them from eating enough to maintain their weight. Cancer might also decrease their appetite and increase their metabolism.
- Bleeding into the esophagus is one more sign of esophageal cancer. This blood then passes through the digestive tract, which may turn the stool black. Over time, this blood loss can lead to anemia (low red blood cell levels), which can make a person feel tired.
- The American Cancer Society’s estimates for esophageal cancer in the United States for 2023 is that about 21,560 new esophageal cancer cases were diagnosed (17,030 in men and 4,530 in women). There was about 16,120 deaths from esophageal cancer (12,920 in men and 3,200 in women).
- Esophageal cancer makes up about 1% of all cancers diagnosed in the United States, but it is much more common in some other parts of the world, such as Iran, northern China, India, and southern Africa.
Barrett’s esophagus is one of the conditions known to lead to the formation of esophageal cancer. Doctors usually refer to this condition as a precancerous problem, since these patients are at increased risk of developing esophageal cancer.
Acid reflux and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) patients whose stomach acid has damaged the esophagus over time are found to be very likely to suffer from Barrett’s esophagus. Some 30% of these patients are seen to develop esophageal cancer and this is why this problem is considered to be one of the first signs of cancerous changes in the esophagus.
Treatment for Esophageal Cancer
After proper diagnosis patients suffering from esophageal cancer are usually advised to undergo surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, to treat the problem. Surgical procedures are able to remove cancer together with some portions of the esophagus or remove some other tissues if the cancer has spread further.
Chemotherapy can be used before or after surgery and some patients may also benefit from added radiation therapy as well.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...