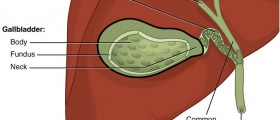
A bile duct is the tube that carries bile. Bile is distributed through the bile ducts from the liver to the gallbladder and from the gallbladder to the small intestine. Bile ducts can become blocked due to gallstones and other reasons. This condition is known as bile duct obstruction. Bile Duct Obstruction
Bile is a liquid that aids in process of digestion and mainly contains cholesterol, bile salts and pigment bilirubin. Bile is produced by the liver and through the bile ducts it is carried to the gallbladder. The gallbladder stores bile and after a meal it releases bile into the small intestine where it aids in breaking down fat. If the bile ducts become obstructed, bile builds up in the liver, which results in elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood. This leads to yellowing of the skin (jaundice).
Causes of Bile Duct Obstruction
There are several possible causes of bile duct obstruction. Bile duct can be blocked due to presence of cysts on the common bile duct. Gallstones and bile duct stones are frequently the cause of bile duct obstruction. Injury from gallbladder surgery, enlarged lymph nodes in the porta hepatic and inflammation of the bile ducts can also cause the condition. In people with weak immune system, bile duct obstruction can be caused by infections. Finally, tumors that have metastasized to the biliary system, bile duct tumors as well as pancreas tumors can lead to bile duct obstruction.
Risk FactorsSeveral conditions can increase the risk of developing bile duct obstruction. People with history of gallstones, chronic pancreatitis or pancreas cancer are prone to bile duct blockage. Recent bile duct cancer or recent biliary surgery can increase the risk as well. People who have had an injury to the abdominal area are also susceptible to obstruction of the bile ducts.
Symptoms of Bile Duct ObstructionSymptoms associated with blockage of the bile ducts include:Dark urine due to excreted bilirubin in the urinePale-colored stoolsPain in the upper right portion of the abdomenFeverItchingJaundiceNausea and vomitingDiagnosis of Bile Duct Obstruction
A doctor usually first examines a patient’s abdomen to palpate the gallbladder. If the doctor suspects bile duct obstruction, he or she orders blood tests that measure bilirubin level, alkaline phosphates level and liver enzymes. The doctor also uses imaging tests such as abdominal ultrasound, abdominal CT scan, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA) and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Amylase blood test, gallbladder radionuclide scan and urine bilirubin can be also used as the diagnostic tests.
Treatment of Bile Duct ObstructionTreatment for blocked bile ducts depends on the underlying cause. Surgical treatment may be needed when the obstruction is caused by gallstones or stones can be removed during ERCP using an endoscope. The blockage that results from cancer is treated by widening of the duct in a procedure known as endoscope or percitaneous dilation. In this procedure a tube is inserted to allow the drainage.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000263.htm
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/gallstones/complications/
- Photo courtesy of Nevit Dilmen by Wikimedia Commons: en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:3DPrinted_biliary_system_20151201.jpg













Your thoughts on this
Loading...