
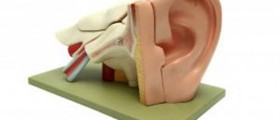
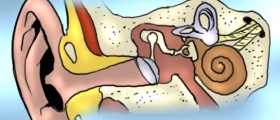
The human ear is anatomically divided into the outer, middle and inner ear. If any of these parts get infected by bacteria, viruses or fungi, there might be some hearing problems. However, some infections of the Eustachian canal or ear canal may also lead to deafness.
Causes of Ear Infection
Upper respiratory tract infections, changes in air pressure during plane travels, swimming in polluted water or even too much cleaning of the ears can all be causes of ear infection and impaired hearing. Some people might have Eustachian tubes of smaller size than it is considered to be normal and this could also lead to development of deafness due to repeated infections. Cleft palate and very young age additionally make babies and children susceptible to ear infections of different types.
Talking about possible infections, deafness may result from otitis (inflammation of the ear) externa, otitis media, serous otitis media, some infectious myringitis (inflammation of the eardrum), acute mastoiditis (inflammation of the mastoid cells), herpes zoster infection of the ear or vestibular neuronitis (inflammation of nerve cells). Out of all of these, otitis externa and media, along with infectious myringitis are more commonly seen to cause hearing loss.
Otitis Externa
This infection is frequently referred to as “swimmer's ear”, because people could catch it by swimming in polluted water or by excessive ear cleaning. Treatment usually comprises a course or antibiotic pills, some antibiotic ear drops, professional cleaning of the ear canal, anti-fungal medications (if the infection is of fungal origin) and pain killers.
Otitis Media
Otitis media can be either acute or chronic problem and is also known as glue ear.
Acute otitis media is common among children suffering from cold or blockage of the Eustachian tubes. In most cases viruses and bacteria are responsible for this infection which can be treated by antibiotic drugs, some ear drops for pus in the ear canal and pain killers if the patient needs those.
Chronic otitis media can be caused by frequent attacks or one lingering attack of acute otitis media. This problem can get complicated and lead to burst of the eardrum, damage to the middle ear, meningitis, labyrinthitis, facial paralysis or sensorineural deafness. Treatment includes aggressive therapy against infection, topical antibiotic drops, sometimes steroids, prevention of another infection and surgical repair of the perforated eardrum.
Serous otitis media is common in kids from 6 months to 2 years of age. It starts as a middle ear infection accompanied by additional accumulation of pus in the ear, so the treatment is usually in a form of a course of antibiotics or surgery which drains the pus.
Infectious Myringitis
This is inflammation of the eardrum, caused by viral or bacterial infection. It can induce a lot of pain and fever and doctors usually prescribe antibiotics, pain killers and sometimes professional rupturing of the blisters formed in the eardrum.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...