
Bad news for fat, good news for the liver
If it turns out that study results obtained by a team of researchers at Children's Hospital in Boston is confirmed in humans, it would be good news for anyone who is suffering from the condition known as fatty liver. More precisely, it would be possible to switch to a dietary regime that might serve to treat or possibly even prevent the disease.
Why is fatty liver disease dangerous?
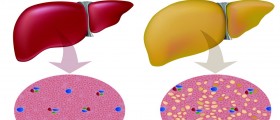
Fatty liver disease, the nonalcoholic variety in this case, is the number one liver disease in the United States. Fatty liver disease has two stages that are determined by biopsy results (biopsy – taking a sample of the tissue from the patient and examining it for changes on the cellular level). In the first stage of the disease, it is 'only' that excess fat deposits in the cells of the liver. This stage is not dangerous per se as it cannot lead to conditions such as cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancer. The second stage, however, is characterized by advancement of the condition, wherein fatty liver disease causes inflammation and scarring of the liver. This stage is much more dangerous as it has the potential to cause dangerous conditions such as cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Trouble with fatty liver disease is that, in majority of cases, it causes no symptoms, so there is an increased risk, that it will advance into liver inflammation, which can develop into hepatitis and eventually cause liver failure – unobserved.
How to treat fatty liver by food?
Data obtained by research from the Children's Hospital in Boston has shown that dietary changes should consist from avoidance of several problematic types of food. On the first place are high-glycemic foods, as these cause a fast rise in blood sugar levels, which contributes to fatty liver. These are foods such as white bread, white rice, various cereals and sugar. On the other hand, low-glycemic foods, that cause a much better, gradual rise in blood sugar levels are vegetables, fruits, beans and grains and other similar foods.
Fat and fatty liver
The common belief is that eaten fat goes into liver and thus most fatty liver diets were low fat diets. This turned out to be ineffective method of treatment in children with fatty liver, and a low-glycemic foods diet is likely to be recommended as better treatment.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...