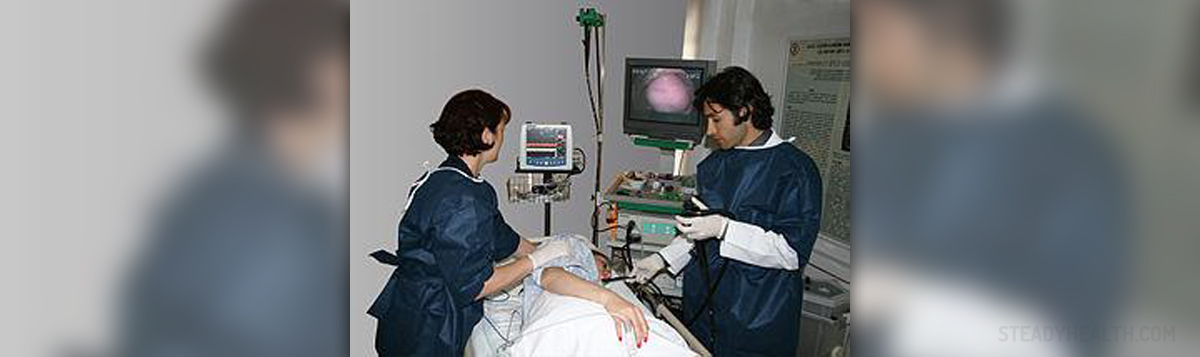
Endoscopy is a medical procedure of internal examination. Endoscope is a small camera probe on top of thin elastic fibre optical wire. There is also s wireless version of endoscope. The probe is inserted into the body orally, rectally, through urethra (urine canal) or through a small surgical incision. The patient is asked to avoid eating and drinking before endoscopy examination.
Depending on the area that needs to be examined a laxative might be given to the patient to clear the bowels. Some cases can include giving the patient a dose of antibiotics to avoid infection.
When the procedure begins, intestines or stomach are filled with air. This can cause mild discomfort.
Sedation during Endoscopy
Sedation in endoscopy procedures is used to avoid or ease the discomfort a patient might feel. During endoscopy sedation used mostly leave the patient awake. Deep sedation is used in very few cases. The anaesthetic used for deep sedation is often propofol and it requires patient monitoring during the procedure. Because of this additional anaesthesia personnel may be required, which increases the cost of the procedure.
Sedation is administered through veins in most cases. A patient can request an endoscopy without sedation.
Sedation used in endoscopy is very safe. Sedation complications are extremely rare and occur in less than 1 in 10 000 cases. The complications usually include temporary hearth or breathing rate decrease. This is caused by low oxygen levels in blood, which is caused slow or shallow breathing by patient. The oxygen levels can be controlled by giving the patient extra oxygen through mask or a tube applied to nose. If a complication is sedation related, counter sedatives can be given through a vein to reverse the process.
The Endoscopy procedures including sedation are performed by trained medical personnel. They monitor the patient’s state vigilantly and regularly both during the procedure and recovery. By following pulse, blood pressure and oxygen levels the doctor and staff are aware of the patients state at all times, ready to react if any complications arise.
The doctor is familiarised with the patient’s medical history, any medications used, and allergies prior to the procedures beginning. With this knowledge the doctor can determine the course of the procedure and what medicine to use.
After endoscopy
The sedation usually outlasts the endoscopy procedure. This means that patient’s reaction time and judgement may be reduced until the sedation effects wear off. Therefore the patient is not in the state to drive and should be accompanied by a family member or someone close.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...