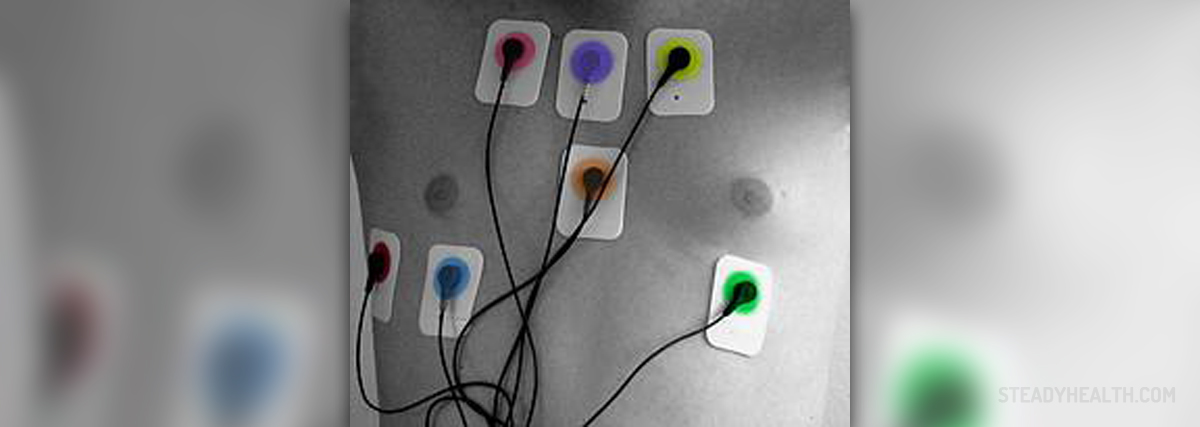

ECG Heart Test
Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a type of test which determinesthe electrical activity in the heart. The heart is a muscle which pumps theblood into organs, other muscles, and tissue. A sinoatrial node is the heart’spacemaker which makes it contract. The ECG identifies and records theelectrical impulses which characterize the heart’s beating. If there are anydisturbances in the heart’s rhythm, they will be caught by the ECG. Abnormalpumping is usually a sign of a heart condition. In addition to being used for diagnosticpurposes, ECG is often employed in determining how well a patient isreacting to medications or another form of therapy. There are various symptoms forwhich individuals are advised to have an ECG. For instance, anyone who can feeltheir own heart beat should seek medical attention. Also, persons who aresuffering from chest pain and breathing problems are usually sent to get an ECGtest. If there are any anomalies in the coronary arteries they will show in theECG. On the other hand, if the ECG is performed while an individual is notmoving there is a strong possibility that the test will not detect anynarrowing of the arteries even if it is in fact present. Subsequently, if amedical care professional wants to rule out or confirm a diagnosis of narrowarteries, the patient needs to be tested while in motion, or preferablyexercising. In addition, once the individual is prescribed medications forcoronary artery problems the results are observed through another ECG test.Also, the test is utilized in discovering any missed or previous heart attacks.In persons who have been battling high blood pressure for a long time it ispossible that the heart starts to thicken, which can also be observed throughECG. It should be noted that there are instances in which anECG yields normal results and misses an underlying heart condition. Therefore,other diagnostic criteria should be used following an ECG for assessing heartproblems. For instance, a radioisotope perfusion scan is one of the additional hearttests that is usually coupled with an ECG. The radioisotope perfusion test isperformed using a low dosage radioactive dye which reveals the areas of theheart with the most and the least blood supply. X-rays of the arteries are alsosometimes performed in order to come up with a precise diagnosis. When it comesto the characteristics of the ECG testing they depend on why the test is beingperformed in the first place. In most cases the test is taken while theindividual is motionless unless the coronary artery disease is suspected. Insuch an instance the patient is usually asked to run on a treadmill for thepurposes of testing. Anywhere between a few to up to 12 adhesive electrodes areplaces on the person’s chest, legs, and arms during the course of an ECG. Someof the areas, such as the chest for instance, need to be hairless and cleanedbefore the test can begin. No sensation is felt during the testand it only takes a few minutes. The results are displayed on a paper printout. Usually there are no side effects associated with an ECG test, but anindividual with a more serious underlying heart condition may experience chest painafter having stopped running on a treadmill. If it happens that the person’sblood pressure drops or the chest pains are strong while still running, the testwill be stopped.
Fitness and ECG
Other than being used for diagnosing heart problems, anexercise ECG is used to monitor changes in the heart while an individual isexercising to determine the level of fitness. Aside from running on a treadmillthe person being testing could also be pedaling on a stationary bicycle. Inorder to determine either the level of fitness or to discover a heart condition,the resting ECG is always performed before the exercise ECG and the results arethen compared. If the resting ECG reveals a serious heart problem, the exercise ECGmay not even be performed for the safety reasons. In addition, the test isoften administered in order to determine how is someone who has had a heartattack able to tolerate exercise and to what extent they can be involved inwork outs. For individuals who exercise regularly but experience dizziness, fastheart beats, or fainting, the ECG can be very useful in finding out why such occurrencestake place. For those who have been inactive for a long period of time the ECGcan help determine an appropriate exercise program. The exercise ECG is usuallydone in a hospital, at a clinic, or in a doctor’s office by a qualified medicalpractitioner. Once the results are available they are evaluated by acardiologist, an internist, or the primary health care provider.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...