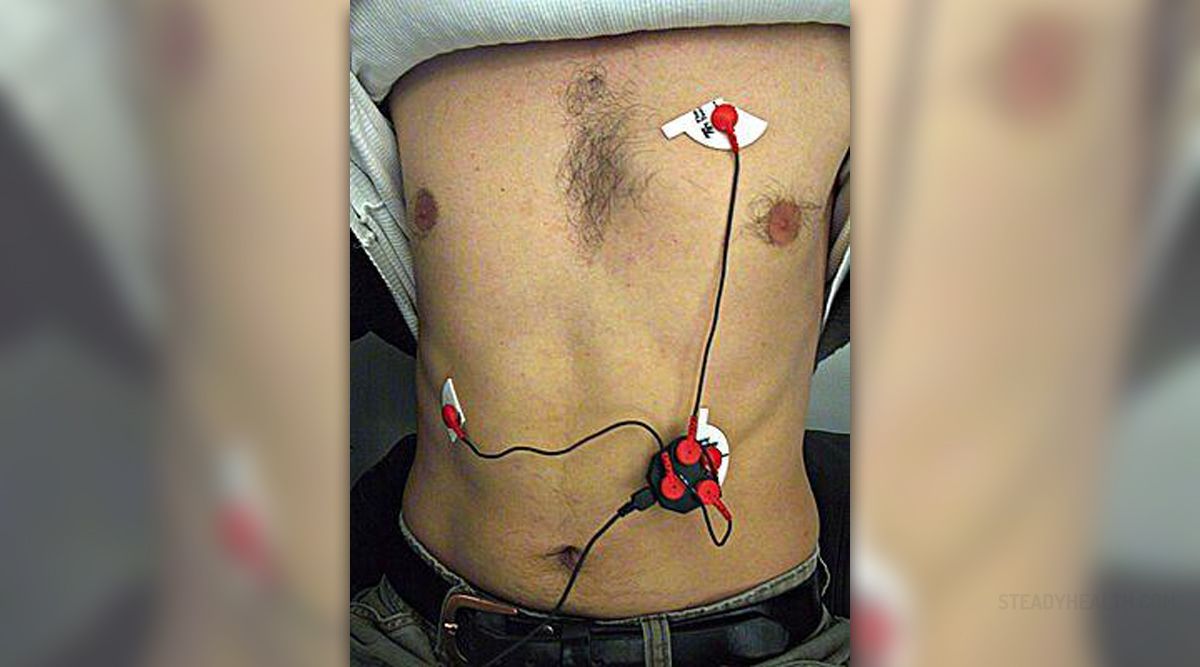
ECG or electrocardiogram is a special sort of test which is conducted in order to show the electrical activity of the patient's heart. The test is done by a machine which collects the necessary information from the surface of one's skin, through specifically placed electrodes. The test records waves which can depict one's electrical activity of the heart through the shape, frequency, rate, regularity and the size of the recorded data.
Problems in the ECG
If the ECG test shows certain irregularities, some sort of a heart condition may be at hand. Arrhythmia, insufficient blood flow to the heart, heart damage because of a heart attack, valve problems, heart enlargement and many other heart anomalies can be perceived through the ECG test.
The Test
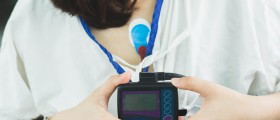
The test is performed by a nurse or other medical practitioner, placing 12 electrodes onto the body of the patient. Specific locations are used for this procedure as the electrodes are placed on the chest, arms and legs, while the patient is lying down. Then, the electrodes are connected to the ECG device which starts the process during which the patient is advised to take deep breaths without moving or talking. The recording lasts for about one minute.
Types of ECG Procedures
Sometimes, ECG test is done while the patient is riding a stationary bicycle. This test is used for differentiating one's heart activity while exercising in comparison to the activity during resting. Coronary artery disease or arrhythmia are diagnosed this way.
Some ECG tests last for up to 20 minutes during which abnormalities are sought. Moreover, a patient may have to wear a holter monitor, which is a small device carried with the patient. Three electrodes get connected to the heart and the portable ECG machine which collects the data. Alternatively, the patient him/herself may activate the device once he/she notices any negative symptoms.
The Purpose of ECG
ECG is one of the cheapest and most precise ways of determining one's heart health. Basically, it can detect ischemia, being a decreased flow of oxygen into the heart due to an obstructions in the arteries, heart attacks, too fast or too slow heartbeats or heartbeats beating at an uneven rate, electrolyte imbalances and other such disorders. Heart sac inflammation, valvular heart disease, enlarged heart, chest trauma and many other conditions, all can be noticed and diagnosed through ECG scanning.
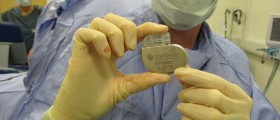
Finally, ECG may test the proper functioning of a pacemaker or the effectiveness of certain heart medications as well as the recovery state after a heart surgery.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...