Dioxins are chemicals created as byproducts of the incomplete burning of waste (garbage) in households or industry. They are also produced during or after bleaching paper pulp and in the production of certain chemicals, such as chlorinated phenols, polychlorinated biphenyls, benzene and some pesticides.
Because dioxins can have very harmful effects on the human body, it is helpful to be able to recognize the symptoms of dioxin poisoning.
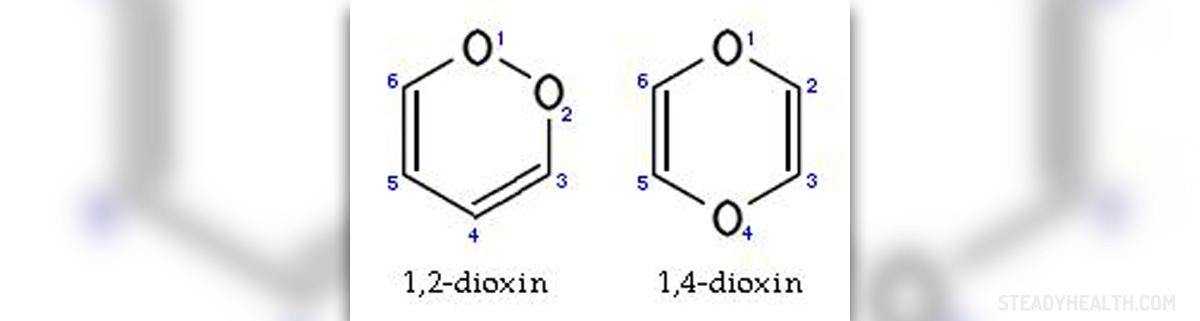
Formation and decomposition of dioxins
Burning wood, for example, in house or forest fires, as well as exhaust gases, also produces dioxins. Traces of dioxins can be found in bleached paper products such as toilet paper, tissues, wipes, paper towels and disposable diapers, but those amounts are considered safe for humans.
Dioxins are released into the air after or during burning. They can contaminate soil and water bodies through rainfall. Plants growing from contaminated soil may contain traces of dioxin and these chemicals can also be found in fatty tissues of animals who fed on those plants or drank contaminated water.
Dioxins do not dissolve quickly in water and rather stay on the bottom, clinging to the sediment. The natural breakdown of these chemicals in the environment is a very long process, and as such, contaminated products will remain unsafe for prolonged periods of time.
Exposure to dioxins: How do humans come into contact with these toxins?
People can be exposed to dioxins by eating meat, dairy, fish or seafood contaminated with these chemicals. Fish and other seafood contains higher levels of dioxin than dairy and meat. As for fruit and vegetables, dioxins may be present on the surface due to the use of pesticides or contaminated dust.
A person can also be exposed to dioxins by breathing contaminated air, especially while something is burning, or through skin contact. Industrial accidents and large fires are considered the biggest hazard when it comes to exposure to dioxins.
Dangers of exposure to dioxins
The effect on dioxins depends on the duration of the exposure, on the route of contamination and on the amount of dioxins a person has been exposed to. Dioxins can cause a skin condition called chloracne, characterized by small, yellowish lesions on the skin. The lesions may go away in a few days or weeks or persist for several years. Several cases have been reported in which exposure to dioxins led to short-term, reversible liver damage.
Even though it is suspected that prolonged exposure to high levels of dioxins may increase a person's risk of cancer, no scientific study was performed to confirm or deny it as of yet.
Toxins can be dangerous for unborn babies and children, and it is suspected dioxin exposure may also have a negative effect on a person's reproductive system, immune system, and nervous system as well.
Tests for dioxin levels
A person suspecting dioxin exposure can get tested. Tests are usually performed on blood, fatty tissue and breast milk but the blood tests have shown to be the easiest and the most reliable way.
All humans are exposed to some level of dioxins, which the World Health Organization considers to be relatively safe, just because these chemicals are present throughout the environment. People who work in agriculture or industries in which chemicals are burned are at risk of being exposed to dangerous levels.

















Your thoughts on this
Loading...