If you have been directed to do an EEG scan, you might be confused and have no idea what this might stand for. If this, indeed, is the case with you, go through the following lines and learn all about the process of electroencephalography.
The EEG, standing for electroencephalography is a process of recording the brain's electrical activity over a course of 20 or 40 minutes. The purposes behind this process are many, depending on the health problem the patient may be suffering from.
Definition
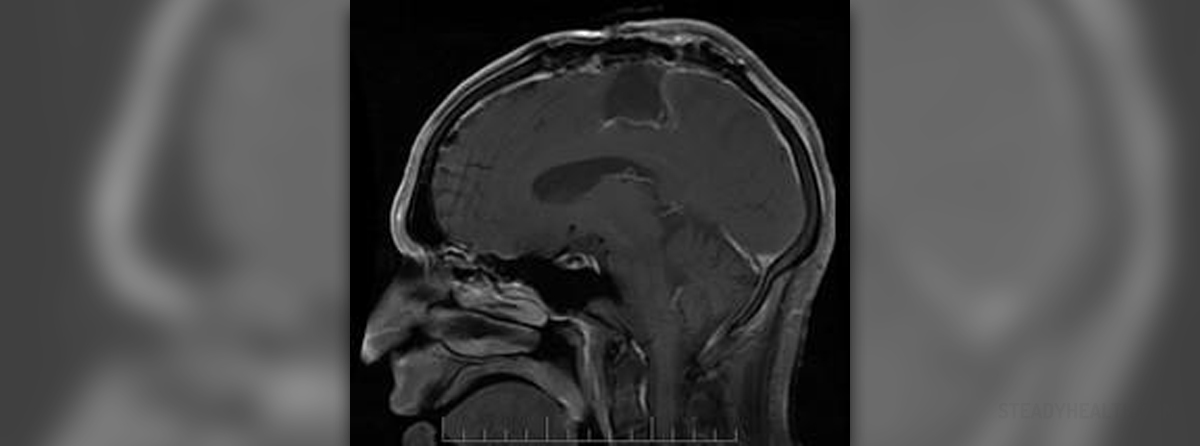
Apart from the above mentioned data, EEG involves placing special electrodes on the scalp of the patient. These electrodes are connected to a computer. They collect the information about the brain's electrical activities while the software in the computer unit transcribes it visually. If the brain signals are abnormal, they can signify the reasons behind a certain health condition such as epilepsy, coma, brain death etc, allowing the health staff to monitor the situation better in order to find adequate treatment.
Furthermore, EEG can be an excellent method for locating brain tumors, strokes and other health issues which involve the brain.
Different Uses of EEG
Basically, the EEG functions on the principle of tracking the electrical activity of our brain's neurons. Since these neurons constantly exchange ions with the cell membranes. This process can be tracked by the electrodes, when they are placed on the scalp of a patient, due to the fact that electrons push one another in a series of waves, allowing the metal of the electrode to conduct this process.
Due to its vast usability, the EEG is used in health facilities in order to help people differentiate their epileptic attacks from other seizures, differentiate different diseases one from another, test the state of brain death, give prognosis for people who are in a state of coma and to determine whether a person needs medications for treating epilepsy or not.
Many sessions of EEG recording are necessary for explaining one's condition and the testing may last for days or even weeks, especially if the seizure itself needs to get recorded.
In some other cases, EEG can also be used for monitoring the strength of certain types of anesthesia. Additionally, it may serve a purpose of an indirect indicator of cerebral perfusion in cartoid endarterectomy. EEG is involved in the process of Wada testing too.
As for the intensive care units in hospitals, these parts too can benefit from having an EEG device, mainly due to the fact that they can record the state of patients suffering from non-convulsive seizures or those who are under anesthesia.
Additionally, EEG can be a valuable tool for researching, expanding the knowledge of neuroscience, cognitive science and psychology, as well as psychophysiology.
Methods
The EEG can be used in many different ways. The most common one involves placing a conductive gel or a paste onto the part of the scalp where the electrodes will be put. Before this part, it is best to remove any layers of dead skin through gentle abrasion. Then, the electrodes or a net of electrodes are placed onto the scalp, each being connected to a different wire. A constant naming system of these electrodes functions and exists on a global level and the number of used electrodes in EEG sessions can range from just a couple, over 19, being the most common usage, to 256.
The montages of the electrodes are different, depending on the condition that is being monitored. Therefore, the electrodes may have a bipolar, laplacian, referential or some other montage.
Even though EEG is an exceptionally useful method of tracking brain activity, it does have several flaws. The main drawback of this method is its lack of sufficient spatial resolution. Due to this flaw, the EEG may not be capable of tracking down the activities taking place deeper inside the cortex, inside sulci, or in other deep areas and currents tangential to the skull.
Nevertheless, statistical researches report that EEG contains specificity of 96.50%, the sensitivity of 95.50%, (97% when it comes to epileptic seizures) and a total precision and accuracy of 96.33%.
Therefore, EEG is widely used in many branches of medical science, being invaluable for many researches and medical processes.
To conclude, the EEG, or electroencephalography, is a process of tracking the electrical activity of the human brain. It is a process used for helping people who suffer from certain health problems which interfere with the mental activities, usually leading to seizures and other issues. For example, people who suffer from epilepsy can find adequate treatment once their doctors perform the EEG.
Even though it has several flaws, the EEG remains an incredibly precise and, thus, valuable method, both for the sake of research in various branches of medical science and for the existing methods of medical treatment.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...