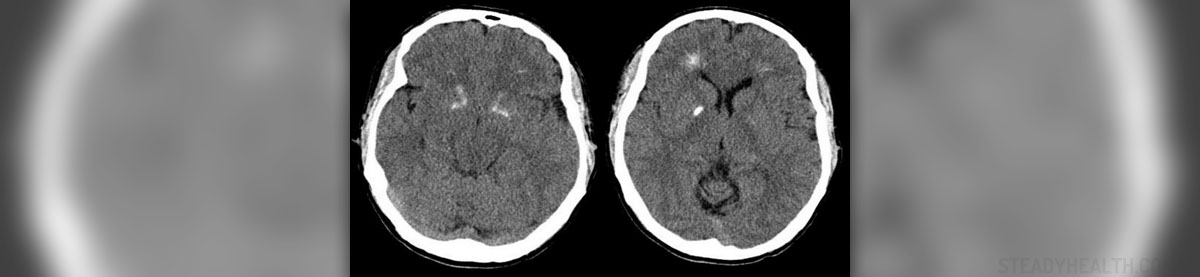
Seizures occur due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain and feature with uncontrollable and repeated twitching of certain parts of the body or the body in general. There are many illnesses and factors associated with the occurrence of seizures. They most commonly affect people suffering from epilepsy, brain tumors and other brain lesions and they may be associated with certain medications, high or low blood sugar, drug withdrawal etc.
There are two types of seizures, partial (focal) and generalized. Partial seizures are further classified into simple partial seizures and complex partial seizures while generalized seizures are most commonly divided into tonic-clonic seizures, absence seizures and myoclonic seizures.
Partial (Focal) Seizures
Partial seizures result from an electrical discharge in one limited area of the brain. They may be associated with head injury, stroke or brain tumors or develop due to unknown reasons. During partial seizures consciousness can be impaired or preserved. Simple Partial SeizuresIn simple partial seizures consciousness is preserved. There is weakness and numbness of certain body areas and changes in taste or smell. The patient may experience twitching of specific muscles or entire limbs, visual changes etc. In case motor symptoms slowly spread from one part of the body to another seizures are in this case classified as Jacksonian epilepsy.Complex Partial SeizuresIn complex partial seizures there is alteration in patient's consciousness. The symptoms are generally similar to those in simple partial seizures. Still the patients cannot interact with the people nearby. There may be automatism in a form of walking in a circle, sitting or standing. Additional symptoms include uncontrollable laughing, unusual thoughts, visual hallucinations and experiencing unpleasant odors.
Generalized Seizures
In generalized seizures larger areas of the brain are affected and the abnormal electrical activity commonly occurs in both brain hemispheres.Tonic-Clonic SeizuresTonic-clonic seizures, also known as grand mal seizures, feature with specific movements of the extremities and/ or face. This may be accompanied by loss of consciousness. Loss of consciousness is generally preceded with a yell or cry. In some patients an aura is an introduction to seizures. The entire body is affected with jerky movements. What follows is drooling, biting of the tongue and the attack ends with bladder or rectal incontinence. After the attack the patients may stay unconscious for an additional period of time. Tonic-clonic seizures last approximately 5 to 20 minutes. After the attack patients feel sleepy and tired.Absence (Petit Mal) SeizuresIn this subtype of seizures there is only brief loss of consciousness without motor symptoms. There is also no aura to introduce the attack. It may appear that patients are involved with the environment and stop what they have been doing. They can stare for 5 to 10 seconds and after the attack normally continue with the initial activity. There is no memory related to the event. In some cases there are subtle motor movements.Myoclonic SeizuresIn myoclonic seizures the attack features with brief jerking movement and it usually affects both sides of the body. The movement varies in intensity. This specific subtype of seizures commonly affects people suffering from juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, West syndrome and Lenox-Gastaut syndrome.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...