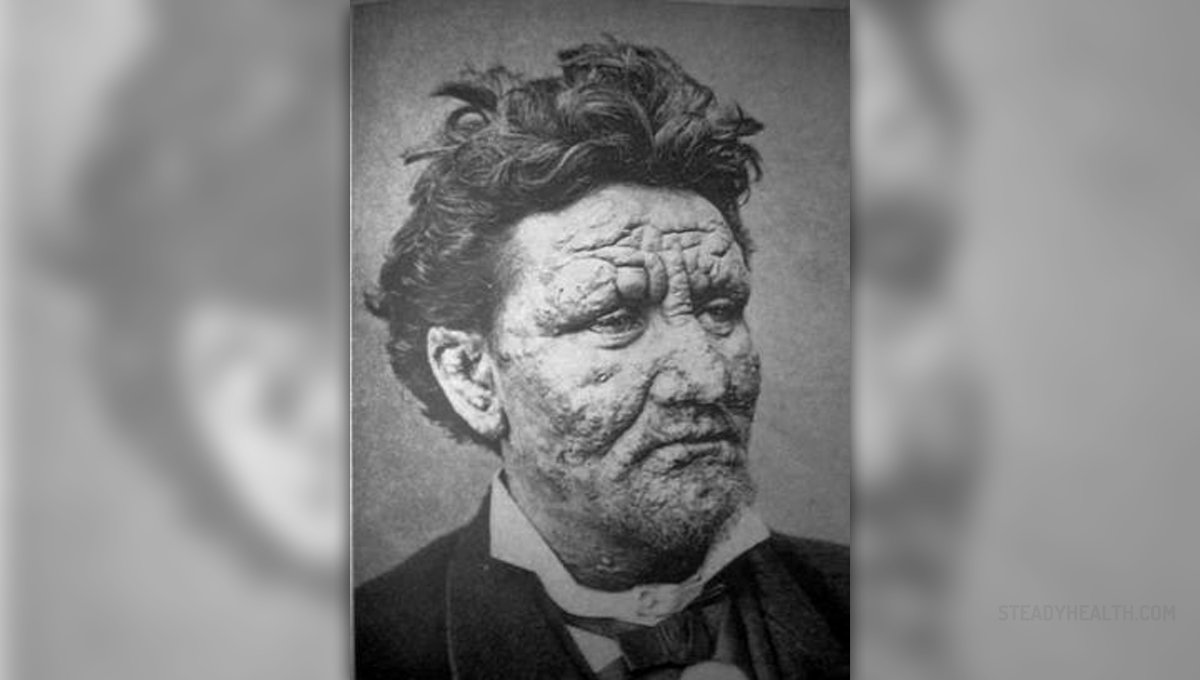

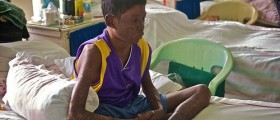
Leprosy is an infectious disease and is one of the oldest diseases in the world. The condition features with disfiguring skin sores, nerve damage and progressive debilitation. Leprosy is found in many countries of the world, particularly in those with temperate, tropical and subtropical climate. In the United States there are approximately 100 cases per year.
What Are Causes of Leprosy?
Leprosy is caused by an infective organism Mycobacterium leprae. The bacterium is not so contagious and is difficult to transmit. The incubation period is long and this makes it hard to determine the actual time when the disease was contracted. Children are more susceptible to leprosy comparing to adults.
Leprosy develops in two forms, tuberculoid leprosy and lepromatous leprosy. These forms can be further divided. Both forms of the disease cause skin sores. Still, lepromatous leprosy is much more severe and leads to formation of large and disfiguring lumps or bumps. Both forms of the infection eventually cause nerve damage in the upper and lower extremities, sensory loss of the skin and muscle weakness. People suffering from chronic leprosy may lose the ability to use their extremities and due to lack of sensation they are prone to repeated injuries.
Clinical Characteristics of Leprosy
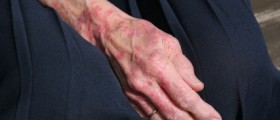
Typical symptoms and signs of leprosy include skin lesions that are lighter than the rest of the skin, lesions that have decreased sensation to touch, heat or pain, lesions that do not heal after several weeks or months, numbness or absent sensation in the hands, arms, feet and legs and finally, muscle weakness.
Diagnosing Leprosy
There are certain tests for diagnosing leprosy. Lepromin skin test is an excellent tool for distinguishing lepromatous from tuberculoid leprosy. The condition can be confirmed after biopsy of the affected skin. And finally, one more test for confirming the disease is skin scraping examination for acid fast bacteria.
Treatment and Care for LeprosySince Mycobacterium leprae may be resistant to certain antibiotics the treatment usually includes a combination of several antibiotics. Three most commonly combined antibiotics include dapsone, rifampin and clofazimine. Claritromycin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin and minocycline are several more antibiotics effective against Mycobacterium leprae. The results are achieved after several months of therapy.
Supportive care can only help with intensity of the symptoms and cannot eradicate the infective agent from the body. Supportive care also includes consultation and treatment provided by orthopedic surgeons, eye doctors and physical therapists. Some of the potential complications of leprosy require specialized footwear, cats and reconstructive surgery. Reconstructive surgery is an essential part of therapy in patients who have developed many disabling complications of the disease. Surgical procedures performed in people with complications of leprosy include tendon transplants to correct clawed hands, reconstruction of nose and eye operation performed to preserve the blinking reflex. Reconstructive surgery is a powerful tool that may make patients look less disfiguring.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...