Information on Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is a yeast infection that occurs in the mouth, and it gets triggered by excessive growth of a certain type of organism called Candida albicans. The organism usually grows on human skin without causing any trouble. It can grow on the skin, but it also grows in the mouth, in the gastrointestinal tract, and inside the vagina.
When the yeast starts growing uncontrollably it may cause pain and inflammatory conditions. This medication condition can be referred to as yeast infection, candidiasis, or moniliasis. Oral thrush can be caused by numerous different factors, and it is always characterized by the uncontrollable growth of yeast.
The most common cause of oral thrush is excessive use of antibiotic medications. Numerous different types of bacteria live on the skin, the intestines, and the vagina, and they are harmless, but they can come in real handy when it comes to competing and fighting off excessive growth of yeast.
When a person takes antibiotics to kill off the bacteria that cause the disease, the harmless bacteria get killed as well. Yeast does not get affected by antibiotics, so it can multiply and grow uncontrollably.
Certain types of cancer medications and steroids may also trigger the flourishing of yeast. Oral thrush is commonly associated with numerous diseases that affect a weakened immune system, such as AIDS and cancer. It is not uncommon in people who suffer from diabetes. It can also be triggered by an unstable mouth environment that can be caused by certain types of medications, especially inhaled corticosteroids.
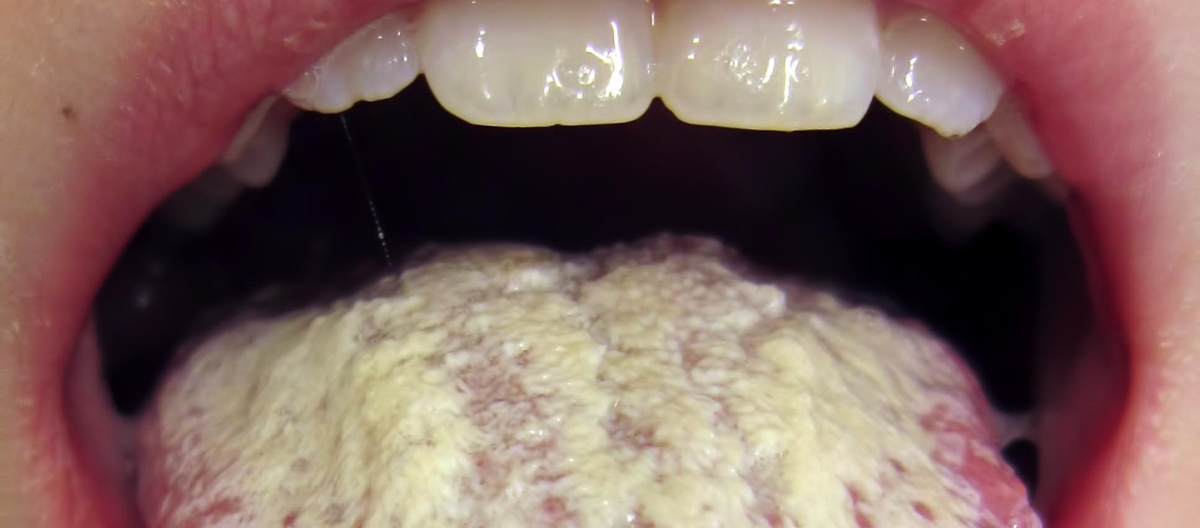
Oral thrush can easily be identified by certain common symptoms such as white patches that cover the oral cavity and red, cracked areas that appear at the corners of the mouth and the skin that surrounds the mouth.
Those white patches may sometimes be rather painful. To diagnose the condition properly, the doctor needs to know about the patient’s diet and the history of antibiotics use. Oral thrush is not a severe condition unless the yeast enters the blood because it may spread to vital organs. It is usually treated with different types of antifungal medications.
- The objective of the present study was to retrospectively survey the demographic and clinical profiles of 1,534 patients diagnosed with candidiasis and treated at the Center for Diagnosis of Oral Diseases (CDOD), Pelotas Dental School, Federal University of Pelotas between 1997 and 2014.
- Using a retrospective, cross-sectional, epidemiological design, data on race, gender, age, systemic diseases, oral candidiasis type and location, symptoms, and harmful habits such as smoking and alcohol consumption were collected. The statistical analysis was performed using STATA version 13.1. Risk factors for chronic atrophic candidiasis (CAC) were evaluated using Poisson regression with robust variance (p ? 0.05).
- The majority of patients with oral candidiasis seen at the CDOD over the 18-year period of analysis were Caucasian women, aged 51–60 years, nonsmokers, and nondrinkers, with no systemic disease, and who wore some form of dental prostheses. CAC was the single most common clinical type of candidiasis detected, and the most frequently affected oral site was the palate.
- Candidiasis is often asymptomatic or may cause some discomfort for the patient, such as stinging, burning, and even pain.
Complications
Oral thrush rarely poses a big problem, but it still can cause serious complications in some cases. People who have cancer or AIDS should take care. Complications of oral thrush may include difficulty feeding, recurrence of the condition, nutrition deficiency, genital thrush, esophagus candidiasis, gastrointestinal thrush, and throat thrush symptoms.




_f_280x120.jpg)











Your thoughts on this
Loading...