Causes of chronic pelvic inflammatory disease
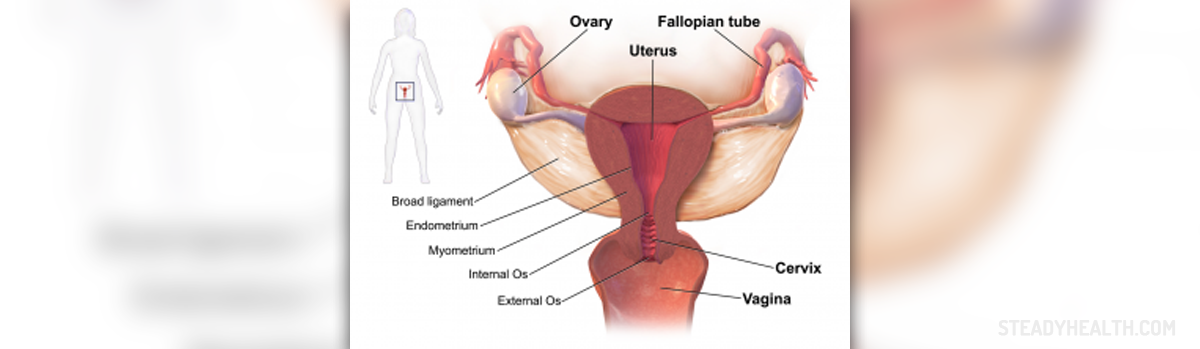
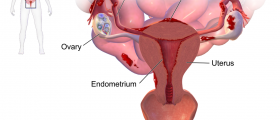
Pelvic inflammatory disease is caused by bacteria that move up from the vagina and affect pelvic organs. Many different bacteria can cause PID but usually those are the bacteria that cause two common sexually transmitted diseases or STDs - gonorrhea and chlamydia. It can take from several days to several weeks until the bacteria move up to the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes and cervix.
PID can also be caused by non-STD infections. For example, the bacteria that are normally present in a healthy vagina can multiply and cause an infection. The exact cause of this is not completely known.
Signs and symptoms of chronic pelvic inflammatory disease
Chronic PID means that a woman is suffering from acute PID symptoms for an extended period of time. The symptoms are not improving and they may in fact become worse. Those symptoms may include fever, foul-smelling vaginal discharge, pain or burning during intercourse or urination, irregular menstrual periods and abdominal pain and cramps.
Diagnosis and treatment for chronic pelvic inflammatory disease
The symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease should be reported to a doctor as soon as they start. That is the only efficient way to avoid having a chronic condition, which can possibly lead to much more serious complications.
The diagnosis for PID is made basing on a physical exam, comprising of abdomen palpitation and internal or pelvic exam, during which the doctor will look for abnormal vaginal discharge, abscesses near or on ovaries or tubes, as well as pain or tenderness of the internal pelvic organs. An ultrasound can also be done in order to get a better view of the pelvic area. Endometrial biopsy and laparoscopy are done in many cases of chronic PID, especially if the disease does not respond to medication.
Pelvic inflammatory disease must be treated with antibiotics. Chronic PID often results from the fact that a woman failed to take all the antibiotics prescribed, or she did not follow the instructions. In severe cases, a woman may need to be admitted in a hospital so her condition can be monitored.
It is also recommended to investigate what is the reason of recurring or ongoing infection. In case there are other factors involved, not just the primary pelvic infection, those factors must be addressed as well.
Chronic PID must be treated thoroughly, otherwise it may cause significant complications, including sterility.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...