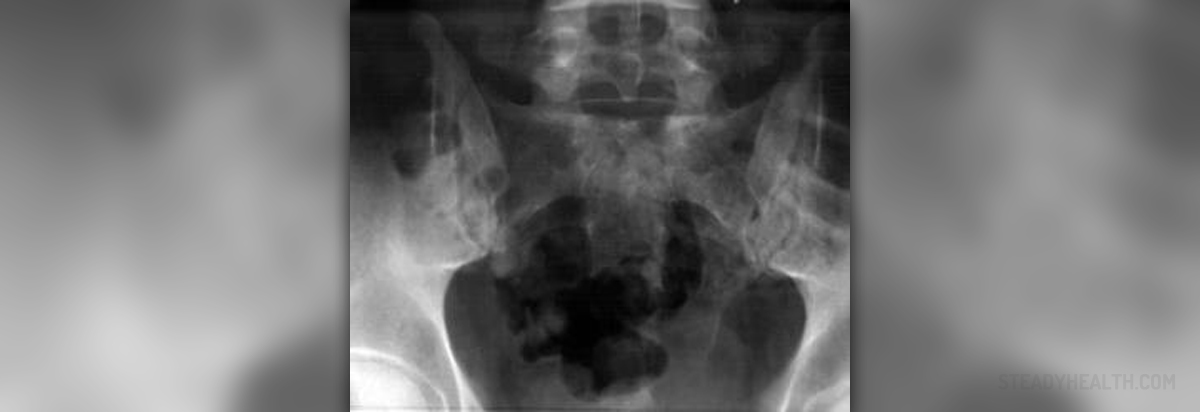
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is in infection that affects female reproductive organs. It usually starts at cervix spreading then towards the uterus, Fallopian tubes, ovaries and surrounding tissue.
Each of these inflammations has its own name: cervicitis is an inflammation of the cervix, salpingitis affects Fallopian tubes endometritis refers to the inner lining of the uterus and peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the lining of the abdomen and the organs that are found there.
In most cases infections that make up the pelvic inflammatory disease are caused either by Chlamidia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which are bacteria that cause sexually transmitted diseases.
In case of salpingitis, the bacteria affect the Fallopian tubes and may lead to the formation of scar tissue. This scar tissue can block the tubes and cause infertility or ectopic pregnancy, which is a pregnancy that occurs outside of the uterus and can be very dangerous.
Pelvic inflammatory disease can cause severe symptoms but it can also be asymptomatic, meaning that there are no obvious symptoms of the illness, which happens particularly with chlamydia infections. This is why it is not always easy to diagnose it and it is important that women who have any symptoms or problems at all see their doctor in order to prevent serious complications.
PID is fairy common as it affects more that one million of women in the U.S. each year, a quarter of which need hospital care.
It is believed that women under the age of 25 and sexually active adolescents are more at risk of pelvic inflammatory disease.
The bacteria that cause PID are usually transmitted through sexual contact and secretions. In more than half the cases PID is caused by the bacteria that cause chlamydia and gonorrhea.
The symptoms of PID include pain in lower abdomen, lower back and pelvis, a vaginal discharge with unpleasant smell, irregular menstrual cycle, pain during intercourse, pain during urination, fever, fatigue, nausea and vomiting.
It is recommended that women seek immediate medical attention of they vomit, have severe pain, have symptoms of shock like fainting and a high fever.
Even if the symptoms are mild it is best to see a doctor. These symptoms, along with genital rash and bleeding between menses can be a sign of a sexually transmitted disease and those should always be treated as early as possible in order to prevent pelvic inflammation disease. Of course if a sexually transmitted disease is diagnosed the patient should act responsibly and inform their sexual partners.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...