Chlamydia trachomatis is a member of one of three bacterial species all of which belong to the genus of Chlamydia. It is a Gram-negative bacterium that enters the affected cells. The bacterium is responsible for many diseases affecting both men and women. For instance, one may develop Chlamydial urethritis, proctitis or trachoma. In men Chlamydial infections may occur in a form of prostatitis and epididymitis while in women there are cervicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease along with complications such as acute/chronic pelvic pain and ectopic pregnancies. The infection, especially if left untreated, is a major contributor to infertility. In neonates Chlamydia is a cause of trachoma, the infection of the eyes that may cause blindness.
Chlamydial Infection Symptoms and Signs
As for men, 1 out of 4 people affected by this infection are completely asymptomatic. If there are symptoms, these are rather similar to gonorrhea symptoms. So, basically, men may complain about burning sensation during urination, discharge from the penis or rectum and testicular tenderness/pain.
Approximately 30% of all women will have symptoms of Chlamydial infection. These include burning sensation during urination, painful sexual intercourse, rectal pain or discharge and symptoms of PID (pelvic inflammatory disease).Diagnosing Chlamydial Infection
In order for the infection to be confirmed, doctors take samples of the urethral discharge in men and cervical secretions in women. If any gender is also prone to anal sex, samples from the rectum are taken as well. Sometimes urine samples are taken too. The obtained samples are sent further to a lab where they are analyzed by monoclonal antibody test, DNA probe test or cell culture.
It is estimated that Chlamydia trachomatis infection usually affects the urogenital tract while in newborns the infection is located to the eyes (ophthalmia neonatorum). Chlamydial pneumonia affects babies between 1 and 3 months of age.Uncomplicated Chlamydial Infection Diagnosis and Treatment Options
In women this type of infection is basically located in the endocervix. Some women may experience odorless and mucoid vaginal discharge without associated pruritus. Gynecological exam reveals inflammation of the cervix and the presence of yellow or cloudy mucoid discharge. The affected cervix may bleed while taking swabs. Clinical microscopy and the amine test are of major importance when differentiating Chlamydial infection from other lower genital tract infections (bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis etc.). Culture techniques are most suitable for detecting the infectious agent.
In men uncomplicated Chlamidial infection basically occurs in a form of urethritis and sometimes epididymitis. Men, similarly to women, report the presence of clear, mild to moderate urethral discharge, easily noticed in the morning. The way to confirm this infection in men is by applying the nucleic acid amplification technique.
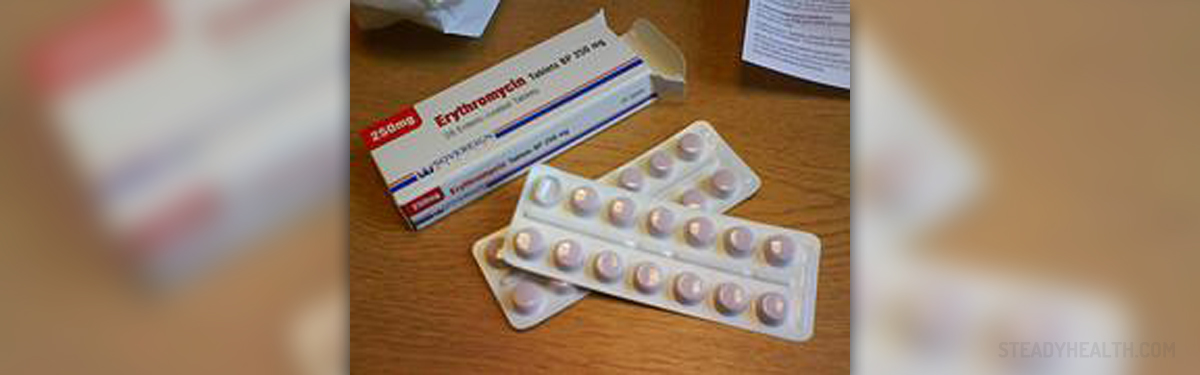
Treatment for uncomplicated cases of Chlamydial infection in both genders (adult patients) includes azithromycin 1g orally in a single dose or doxycycline 100mg orally, twice per day for 7 days and sometimes patients undergo treatment with erythromycin base, erythromycin ethylsuccinate, efloxacin or levofloxacin.
Treatment for PID caused by Chlamydial Infection
Treatment in case of this complication of Chlamydial infection is performed on an outpatient basis. Only pregnant women as well as women who have developed severe illness accompanied by nausea and vomiting, high fever or tubo-ovarian abscess are hospitalized. Such patients are treated with ofloxacin 400 mg twice per day, for 14 days. Patients may also be administered levofloxacin 500 mg orally once per day for the same period of time. Alternative treatments include ceftriaxone with probenecid or doxycycline with metronidazole. Parenteral treatment includes cefotetan, clyndamycin or ofloxacin.
Treatment for Pregnant Women
Certain antibiotics are strictly forbidden during pregnancy. Therefore, women suffering from Chlamydial infections are prescribed either erythromycin base or amoxicillin. The later drug is more efficient and also has fewer side effects. Pregnant women undergo a repeated test after completion of treatment (three weeks after the last dose of the prescribed antibiotic).
Treatment for Chlamydial Infections in Children
Ophthalmia neonatorum occurs during vaginal delivery when the mother is suffering from active Chalmydial infection. The disease affects the child's eyes and the first symptoms develop 5-12 days after delivery. The infection leads to swelling of one or both eyes and there is mucopurulent drainage.
The infection is easily confirmed by culture or nonculture techniques and treatment comprises erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate at a dose of 50 mg per kg per day. The antibiotic is taken orally, four times per day for 14 days.
Treatment for Chlamydial pneumonia consists of erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate and is administered in the same dose and under the same circumstances as it is in case of ophthamia neonatorum. Both of these infections may require a second course of antibiotics.Chlamydial Infection Relevant Data
This STD is actually the most reported one in the United States. Because of that, sexually active females who are 25 years old or older are recommended to be tested every year.
On the global level, Chlamydial infection affects approximately 92 million people each year (50 million women and 42 million men). Left untreated this STD may cause serious complications out of which infertility and blindness are the most severe ones.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...