Gonorrhea is one of many STDs affecting both genders. This infection is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a Gram-negative bacterium. After being contracted, the bacteria may start to multiply in different parts of the urogenital and anal area including the cervix, urethra, rectum and in people who have had unprotected oral sex with infected individuals even the throat can be affected.
Fortunately, gonorrhea is highly curable infection and it takes only several days of antibiotic treatment and the bacterium is completely eradicated. Left untreated or inadequately treated, gonorrhea may cause chronic inflammation of reproductive organs, especially in women who tend to develop pelvic inflammatory disease, a condition commonly blamed for abdominal pain and recurrent ectopic pregnancies. Apart from infertility, in neglected cases patients may end up with meningitis or septicemia.
Gonorrhea: Symptoms and Signs of the Infection
In the majority of cases the first symptoms of the infection develop 1-14 days after exposure. It is, however, possibly for one not to develop any symptom at all, which is classified as asymptomatic infection. Symptoms and signs of gonorrhea are more apparent in men.
As for women, gonorrhea is blamed for a change in vaginal discharge, which is present in large quantities and is green or yellow with a strong smell. An infected woman may additionally complain about burning sensation while passing urine, irritation or even discharge from the anus. Pain between periods may additionally point to the presence of the infection, especially if it is otherwise asymptomatic.
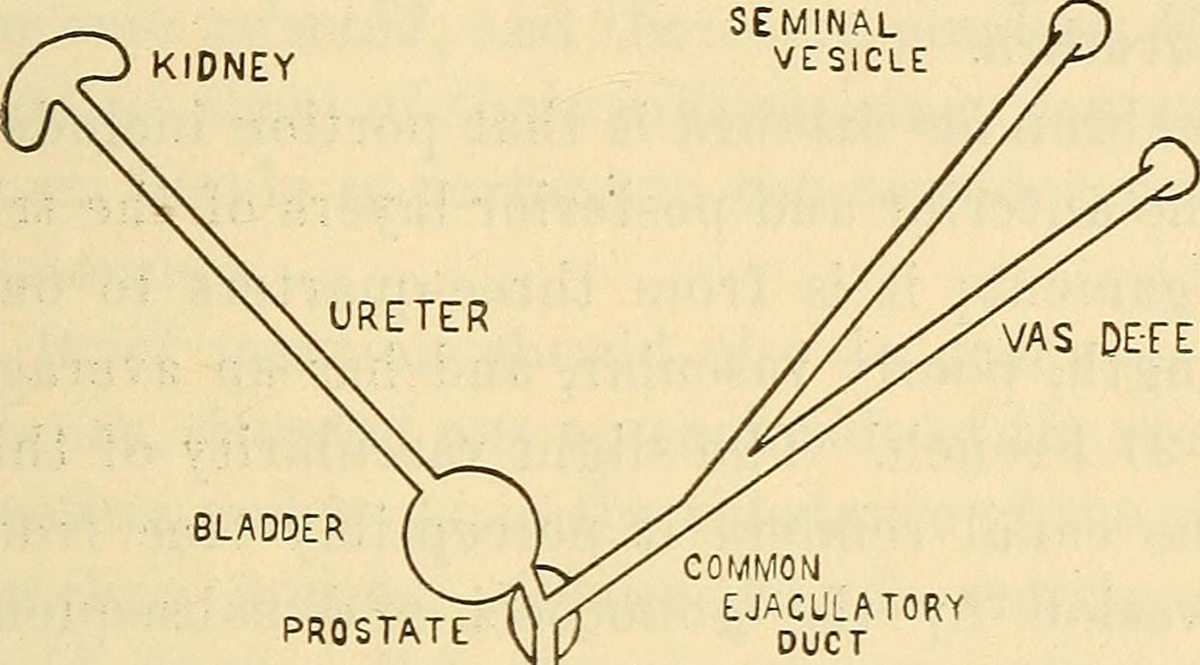
In men gonorrhea is characterized by white or yellow discharge from the penis, burning sensation during urination and also irritation and discharge from the anus. In men Neisseria gonorrhoeae may cause inflammation of the prostate and testes too.
Diagnosing Gonorrhea
In order for the bacterial infection to be confirmed, doctors take samples during physical exam (exam of the genital and anal area). These samples are sent to a lab and tested for the bacterium. The results are available in less than a week.
Samples sent for testing depend on symptoms of infection and may include urine sample, swabs from the cervix, vagina, throat, rectum and penis. Taking swabs may be quite uncomfortable, especially for men, but this part of examination is essential for confirmation of the infection.
Treatment for Gonorrhea
It is not hard to eradicate Neisseria gonorrhoeae because the bacterium is sensitive to many available antibiotics and treatment basically does not last long. Antibiotics are administered in a form of tablets/pills, liquid or injections. Pregnant women are due to report their pregnancy because of proper selection of the drug (doctors prescribe only antibiotics that cannot harm the mother or the baby in her uterus).
Furthermore, once the treatment starts, it is essential not to be discontinued and to be finished as recommended. By cessation of treatment the infection may not be eradicate. This increases chances for complications. Finally, while taking antibiotics all patients are advised to abstain from sexual intercourse. Once, the infection is completely cured they may continue having sex, but with proper protection (latex condoms). All patients must return for a check-up after certain period of time, when doctor performs the test again confirming or ruling out the success of the treatment.
In cases when infection does not respond well to prescribed antibiotics, these are replaced with other medications of this type. It is, therefore, best to use antibiogram and chose antibiotics the isolated bacterium is sensitive to. Sexual partners of the infected individual must be examined and many times treated as well.Gonorrhea Relevant Data
In 1999 there were 62.35 million people affected by gonorrhea. This makes gonorrhea practically the most commonly reported sexual transmitted disease on the global level. The infection was (and still is) reported more in women.
In the period between 1995 and 1999 there was a significant increase in gonorrhea cases in Estonia, Russia and Belarus all of which are countries of Eastern Europe. As for Africa, the highest incidence was reported in Central African Republic and South Africa.
According to statistical data from 2009, there were 301,174 cases of gonorrhea reported in the United States. In 2010 the decline in incidence was noticeable (10%). As a result, gonorrhea was at that time the second most commonly reported STD in the country. Once again women were affected more than men.Gonorrhea Prognosis
Gonorrhea is curable infectious disease and only if not treated properly, or not treated at all may cause certain complications.
In women gonorrhea is a cause of PID (pelvic inflammatory disease) and subsequent risk of ectopic pregnancy and infertility. Also, if the infection is contracted during pregnancy it can be easily passed on to the baby and cause eye infections (common during vaginal birth).
In men, untreated gonorrhea may cause inflammation of the prostate, testes and epididymis, all of which may additionally be blamed for infertility. Untreated inflammation of the urethra is associated with strictures and pain along with additional problems whilst urinating.
All in all, gonorrhea does not have to be contracted at all, if one uses latex condom each and every time while having sexual intercourse.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...