What Exactly Is Chemical Pregnancy?
Chemical pregnancy is a medical condition in which a woman’s pregnancy ends too early, before the fertilized egg has implanted in the lining of the uterus. In such a case the pregnancy test is positive if a woman takes it before she gets her period, but on the other side, if the woman waits for her period, she does not get these results, which is why it can be rather disappointing in case a woman wants to be pregnant. Chemical pregnancy is a medical term for a very early miscarriage and even though it is very common, in the majority of the cases, women are not even aware of the fact that they have been pregnant for a very short period of time. The scientists say that problems in the development of fetus due to certain chromosome abnormalities are among the most frequent causes. Besides that, abnormalities of the uterus of a woman may affect or prevent the implantation of the egg, which will also result in the early miscarriage, while it is also possible that hormonal deficiency in a woman will result in chemical pregnancy. It is practically impossible to prevent chemical pregnancy, though, if it occurs frequently in a woman, it is necessary to identify the cause and treat it.
Symptoms of Chemical Pregnancy
In the majority of the cases of chemical pregnancy there are no symptoms at all, which is also a reason why women are extremely rarely aware of it. Some women may experience signs that are similar to the symptoms of normal pregnancy and such signs include increased breast sensitivity and tenderness, nausea, vomiting and morning sickness. Still, signs that indicate the early abortion are bleeding from the vagina as well as clots in menstrual blood, or an increased blood flow during menstruation. It is very likely that a woman might experience severe cramps in the abdomen, too. Still, hCG levels in the blood may also indicate a chemical pregnancy, which is why women who suspect of this condition should do this test. The greatest number of these cases is not treated at all, but it may be useful to monitor the hCG levels for a few months, because in case they keep on lowering, it may be dangerous for a woman who wants to be pregnant again.Do Uterus Abnormalities Have Influence on This?
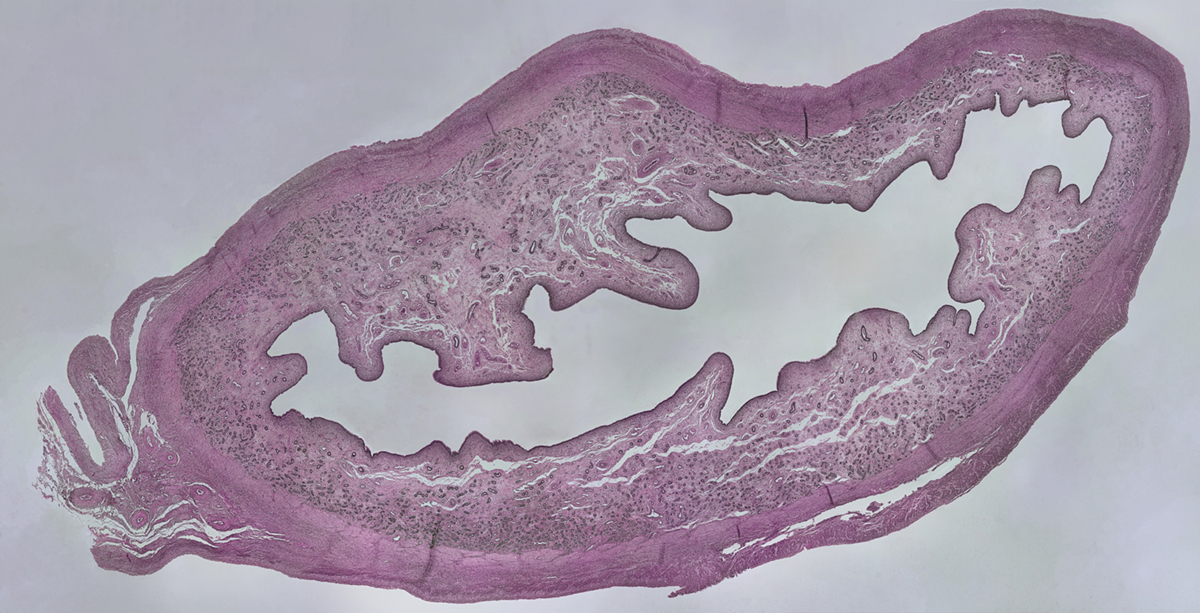
Apart from normal enlargement of the uterus which occurs in pregnancy, numerous medical conditions of this female reproductive organ can lead to its enlargement. This medical condition is rarely asymptomatic particularly if the uterus becomes huge. Enlargement of uterus typically leads to enlargement of lower abdomen and this may be neglected and considered as weight gain. Enlargement of the uterus is sometimes found during routine gynecological examination. Structural and developmental abnormalities are among the leading causes of enlarged uterus. Uterine fibroids can be another cause of uterine enlargement. These benign tumors most commonly affect approximately 50% of all women. Their size may vary from person to person and if they grow large enough they typically cause noticeable uterine enlargement. Women may have one or suffer from multiple uterine fibroids. Even ovarian cysts can be the cause of uterus enlargement. The uterus also becomes bigger in case of endometrial cancer when it grows inside of the uterus and causes its expansion. A medical condition known as adenomiosis is characterized by a presence of endometrium other than its particular place, and it may also lead to enlarged uterus. Adenomyosis commonly affects women in their 30s and is in most cases also accompanied by irregular menstrual bleeding, menstrual cramps and sometimes even clotting during menstruation. Symptoms of an Enlarged Uterus
The symptoms of enlarged uterus may or may not include abdominal pain, intensive menstrual cramps and painful menstruation, weight gain, etc. The biggest problem is that all of these symptoms can be easily overlooked and neglected. Fortunately enough, women who have regular gynecological examination are easily diagnosed even before the onset of symptoms. Enlarged uterus can also interfere in normal menstrual bleeding by inducing a medical condition called menorrhagia which is characterized by significantly profuse or prolonged menstrual bleeding. Additional abnormalities include irregular periods and passing blood clots. Sudden weight gain can also be symptomatic for uterus enlargement. As far as visible symptoms are concerned, an increase in the waistline may particularly point to the enlargement of this reproductive organ. The pain or discomfort caused by uterus enlargement occurs during menstruation, it may also radiate towards lower back or flank area, it may accompany sexual intercourse and be in a form of abdominal pain.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
The enlargement of the uterus can be easily diagnosed by pelvic examination. If the uterus is slightly enlarged this can be detected only with pelvic ultrasound. Further examinations such as biopsy, CT of the pelvis or even laparoscopy are also performed in some cases in order to establish the actual cause of uterine enlargement. Treatment for enlarged uterus basically depends on the actual cause and it may be either conservative or surgical.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...