What is a Menorrhagia?
If woman, during period which lasts less than 7 days, loses more than 80 ml of blood this condition is very close to menorrhagia.
It is hard to measure the amount of lost blood, but if a woman soaks more than one pad an hour, or must put two pads at once, or she must change it at night, if the bleeding has large clots, and if her menstruation disrupts daily activities, such menstruation is certainly considered as menorrhagia.
Causes of a Heavy Period
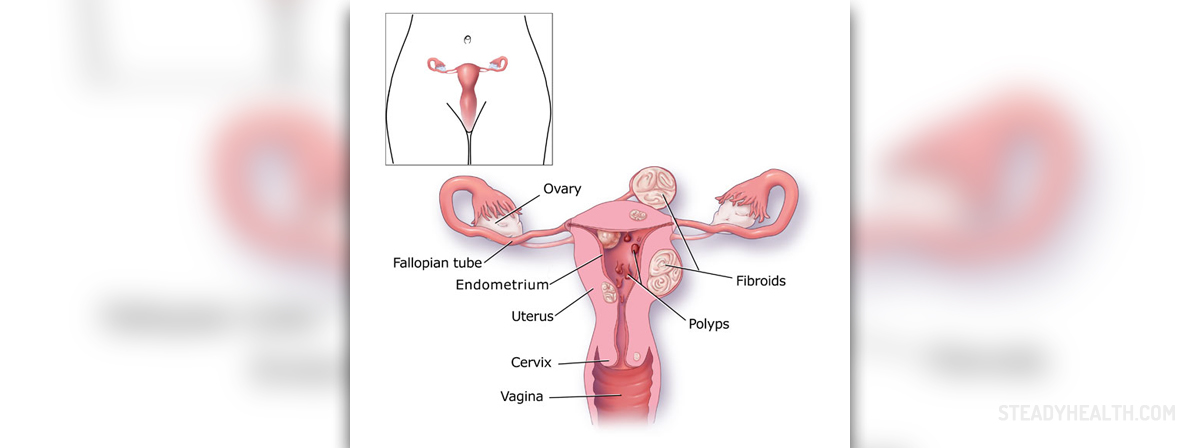
In 80% of cases, heavy periods are a result of hormonal imbalance or uterine myoma.Hormonal imbalance is most common at the beginning and the end of woman's reproductive period. The balance between the hormones estrogen and progesterone allows growth of the uterus lining (endometrium) to a certain level. If there is no pregnancy, mucous membrane peels, performing menstruation. If the endometrium is more thicken, heavier bleeding will perform. Also, uneven mucosa peeling causes extended bleeding.
Myoma is a relatively frequent benign tumor of the uterus, which can lead to an abundant and prolonged bleeding.
Endometrium, ovaries and fallopian tubes inflammation may also be the cause of heavy menstruation.
Hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function) may lead to hormonal imbalance and consequentially to menorrhagia.
Heavy bleeding that occurs a little later than expected period may be due to early spontaneous abortion. If abortion is complete - whole embryo is expelled with menstrual blood, the bleeding will stop spontaneously. If it is not complete, audit of uterine cavity (curettage) should be done.
Other menorrhagia causes include polyps, ovarian cysts, ovarian dysfunction, endometriosis, intrauterine pads (spiral), pregnancy complications, cancer and some medications.
Complications
Menorrhagia is the most common cause of anemia in women, caused by insufficient iron in the body. Anemia causes weakness and fatigue, and in severe cases, rapid pulse, ringing in the ears, headache and decrease the resistance of the organism.Heavy bleeding is often accompanied with severe menstrual cramps. Sometimes the pain is so hard that disrupts everyday activities.
Many conditions associated with the menstrual cycle irregularities, including heavy bleeding, myoma, ovary function disruption, and endometriosis may contribute to infertility in women.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...