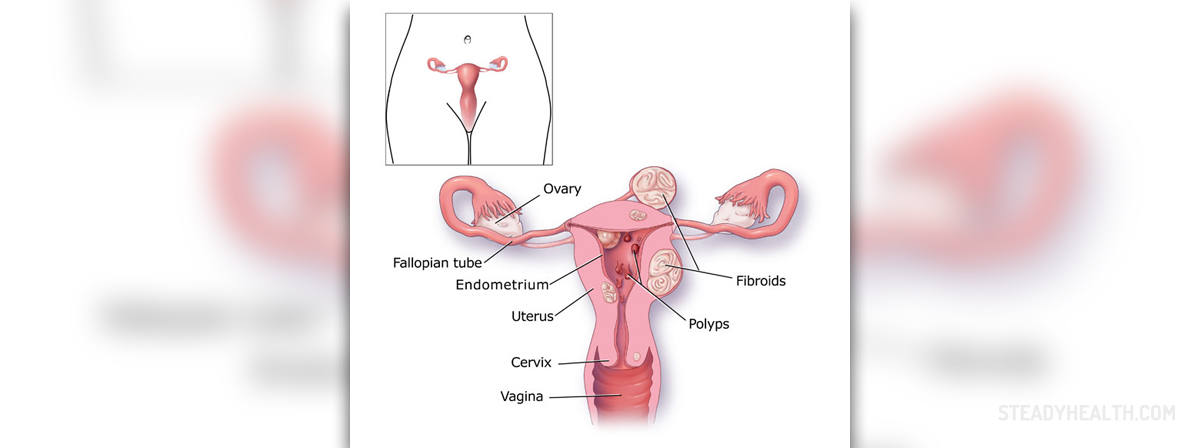
Menorrhagia is an unusually heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding. Sometimes, depending on the cause, menorrhagia is also associated with severe pain. To understand menorrhagia one should first understand that the normal average menstrual cycle lasts from 25 to 35 days. It can be a bit longer or a bit shorter in certain individuals, but these are rare. Menorrhagia is any condition that involves a blood loss, due to a period, greater than 80 ml or a period lasting longer than 7 days. Menorrhagia occurs in normal intervals, while the similar condition known as menometrorrhagia occurs at irregular and more frequent intervals. This condition may sometimes causes enough blood loss and cramping that obstructs woman’s normal daily activities.
Symptoms of Menorrhagia
Normally, a regular tampon fully soaked will hold about 5cml of blood, and a total blood loss during a period is somewhere about 30 to 44 milliliters. If the menstrual flow soaks through one or more sanitary pads every hour, for several consecutive hours, a woman is probably experiencing menorrhagia. Menstrual flow will probably include large blood clots, which occur naturally as a result of passing blood too quickly. Body releases anticoagulants that keep the blood liquid and thinned, but when the flow is extremely strong, the blood passes before the anticoagulants can work. Women may also experience tiredness, fatigue or shortness of breath, which are all symptoms of anemia. The flow may be so heavy that a woman needs to use double sanitary protection or to change it overnight.
Causes of Menorrhagia
Normally, there is no known cause in a particular case. The whole treatment for menorrhagia focuses on treating the symptoms. Most probably, menorrhagia occurs as a result of hormonal imbalances and abnormal buildup of the lining of the uterus. Dysfunction of the ovaries and a lack of ovulation may also cause hormonal imbalance and result in menorrhagia. Uterine fibroids, benign tumors of the uterus or polyps may also cause heavier than normal or prolonged menstrual bleeding.A number of other reasons including adenmyosis, intrauterine devices, pregnancy complications, cancer, inherited bleeding disorders, certain medications and other medical conditions may cause menorrhagia.
Treatment of Menorrhagia
In most cases, heavy periods settle spontaneously and no treatment is required. However, if anemia occurs then iron supplements may be used to help restore normal hemoglobin levels. The condition is often treated with hormones, usually oral combined contraceptive or progesterone only pills. Tranexamic acid tablets may reduce the blood loss by up to 50%, while anti-inflammatory medications cause about 30% reduction in a blood flow.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...