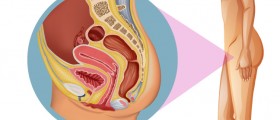
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) is abnormal bleeding from the uterus that may affect women in their childbearing years. However, this bleeding is most commonly seen in women who are either at the beginning or the end of their reproductive years. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is associated with changes in hormone levels.
The menstrual cycle of a woman takes place between 21 to 35 days apart. Women averagely lose 40 to 155ml blood per each menstrual cycle. Shedding of the endometrium occurs during the first days of menstrual cycle. In the following 8 to 9 days follicular phase occurs during which estrogen stimulation causes endometrial proliferation. The ovaries secrete the estrogen with the help of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Then, the ovulation occurs in which the ovarian follicle bursts. This is followed by luteal phase in which progesterone and estrogen are secreted by the corpus luteum until the beginning of the next cycle.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding can be classified into different types. They include:MetrorrhagiaMenorrhagiaMenometrorrhagiaPostcoital bleedingAmenorrheaIntermenstrual uterine bleeding (spotting)OligomenorrheaCauses of Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDysfunctional uterine bleeding can be caused by a few reasons. The condition often results from imbalance between estrogen and progesterone. Improper built up of endometrial lining due to low estrogen levels can cause prolonged bleeding. This can be seen in women who use birth control pills.
However, dysfunctional uterine bleeding is most commonly caused by Anovulatory Cycle featured by increased production of estrogen and absence of progesterone. In avolutatory cycle, the functionalis layer continues to develop until eventually follicle stimulating hormone level drops. This finally leads to irregular and frequent menstrual bleeding, the condition known as menometrorrhagia.
The second leading cause of dysfunctional uterine bleeding is luteal phase deficiency that takes place due to low level of progesterone and low, normal or high level of estrogen. This causes short or irregular menstrual cycle.
The third type of dysfunctional uterine bleeding occurs in women older that 38 years of age. The produced ovarian follicles are of low quality and quantity and cannot make enough estrogen to generate the ovulation. In this condition, production of estrogen does not stop but occur late leading to late cycle.
Other underlying causes of dysfunctional uterine bleeding include endocrine disorder, polycystic ovary disease, hyperprolactinemia, Cushing’s disease, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, premature ovarian failure, uterine polyps, enlarged uterus and structural or malignant lesion of vagina/cervix.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding
Diagnosis of dysfunctional uterine bleeding includes pelvic exam, analysis of basal temperature, urine test, blood test, uterine ultrasound and endometrial biopsy. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding can be treated with medication, surgery or combination of both.
Medication treatment commonly includes oral contraceptive pills, progestin pill, intravenous estrogen or oral conjugated estrogen. Levonogestrel-releasing intrauterine system and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be also used. Surgical treatment can be used if DUB causes severe symptoms. This includes laser endometrial ablation, hysteroscopic transervical resection of the nedomtetrium and hysterectomy.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...