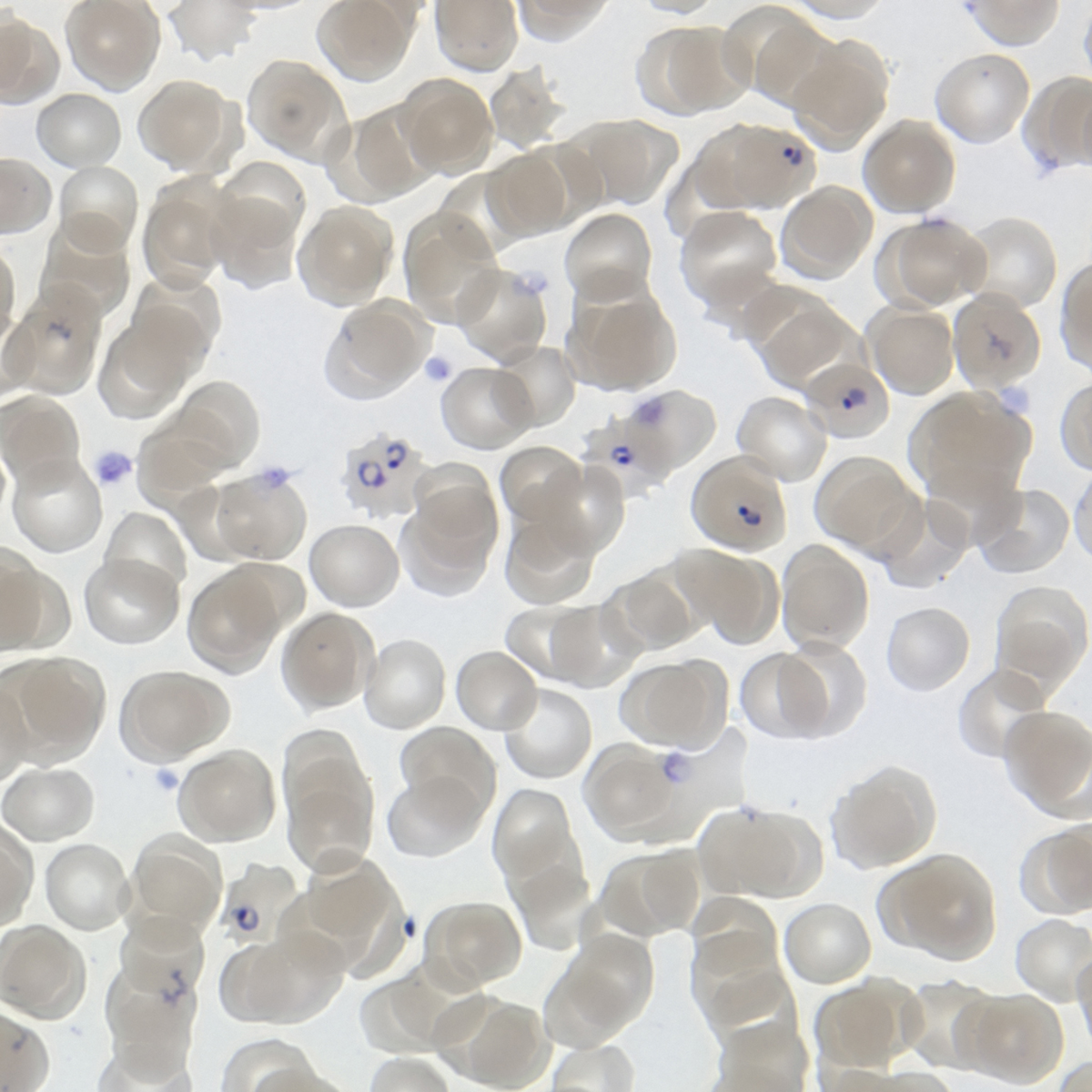
Malaria is a parasitic disease that involves high fevers, shaking chills, flu-like symptoms, and anemia. It is a mosquito-born infectious disease most widespread in Africa, Southern Asia, Central America and South America. Causes
Malaria is caused by a parasite that is transmitted from human to human by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. This is the only kind of mosquito that may be able to spread malaria. The mosquito becomes infected by biting the infected person and further transmits the blood-containing parasite to another person.
Rarely people may get malaria if they are exposed to infected blood. An unborn baby may possibly get the infection from its mother. It is important to understand that malaria does not spread through the air or by normal physical contact. Being near the person who has the malaria is not considered a risk factor.
There are five species of Plasmodium parasites that causes infection to people:Plasmodium falciparum
This parasite is found mostly in the tropics and subtropics (near the equator). It is often resistant to a popular antimalarial medicine (chloroquine) and needs treatment with other medicines.
Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium knowlesi
Infection with Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium malariae is most common in all of the tropical regions of the world. Plasmodium ovale is found in western Africa while Plasmodium knowlesi populates Southeast Asia regions. Infection with Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium ovale is usually not life threatening and patient may recover after a couple of months of treatment. On the other hand, Plasmodium knowlesi infections may often be fatal. These parasites are generally not drug-resistant as Plasmodium falciparum, but they may stay in the liver requiring further medical treatment in order to avert relapses.
Symptoms
Symptoms of malaria are similar to flu symptoms. They include a high fever, chills, and muscular pain. Fatal type of malaria may cause more serious symptoms such as damage to the heart, lungs, kidneys, or brain.
Treatment and prevention
Malaria is a preventable disease that may be avoided by taking medicine before, during or after traveling to areas of the world where malaria is present. However, prevention is not completely effective. Parasites may become resistant to certain medicines, and if this is a case, medicines will not stop the infection.
It is important to consult a doctor right away if one experiences flu-like symptoms in the area where malaria is present and if one has been exposed to mosquitoes. There are some effective medicines available to treat the illness and prognosis for recovery is quite good in most of the cases.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...