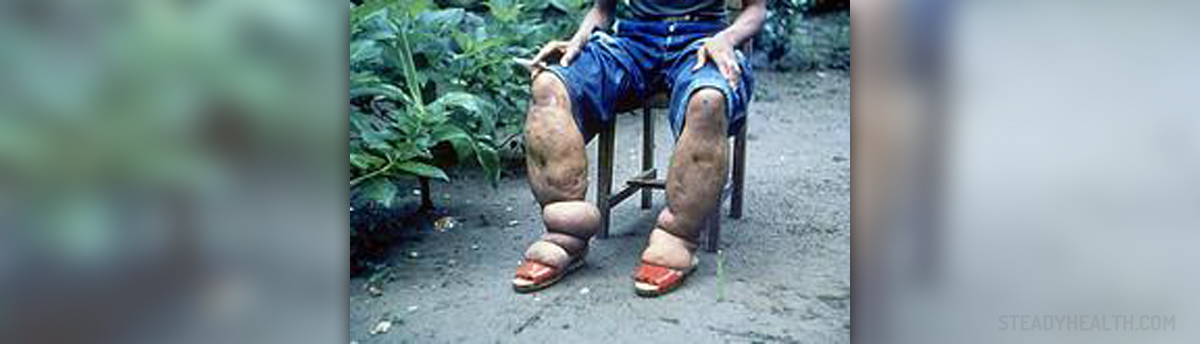
Filariasis, to be more precise, lymphatic filariasis is a parasitic infection caused by thread-like filaria nematodes. These parasites enter one's lymphatic system (both lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes). Their presence is a cause of obstruction of lymph flow which eventually leads to swelling and typical changes on the inadequately drained tissues. The major problem is related to inadequate drainage of lymph from the lower extremities. As a result the entire legs (in men even the scrotum) enlarge to abnormal size. This complication of the disease is known as elephantiasis.
Transmission of the Parasite
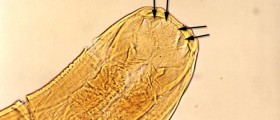
The parasite responsible for this infection is easily transmitted through a mosquito bite. The infected mosquito carries larvae which, once they enter the lymphatic system, soon mature into adult worms. These can live up to 4-6 years. Female worms are capable of producing millions of larvae. They are found in the bloodstream only at night when after a bite of a mosquito they can be easily transmitted to a new host. In many cases, a single bite does not lead to infection. So, only after a series of bites one may develop this debilitating disease. This drives to conclusion that people who spend most of their time and remain active outdoors at night as well as those who are in remote jungle areas of the endemic regions are at higher risk for developing filariasis infection.Filariasis Treatment
Filariasis is treated with ivermectin, albendazole or diethylcarbamazine. These medications are efficient when it comes to killing larvae, impairing the adult worms' ability to reproduce and killing adult worms. The doses are initially low because the death of too many parasites may cause serious body reactions. All the side effects associated with the massive death of parasites are controlled by antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids.
Unfortunately, patients who have already developed elephantiasis may only benefit from surgical removal of surplus tissue and support with elastic bandages. The prognosis of filariasis, therefore, depends on the time when one is diagnosed with the condition and the onset of treatment. Mild cases completely respond to treatment and the prognosis is in such cases good, particularly if there is no re-infection.Filariasis Prevention
The only way to prevent filariasis is to prevent being repeatedly bitten by infected mosquitoes.
The most suitable precaution methods are to limit outdoor activities that take place during the night and limit time spent in rural/jungle endemic areas. If the mentioned is not possible, one should wear long sleeves and pants and stay away from dark-colored clothing which seems to attract mosquitoes. One should also stop using perfumes and colognes and instead start wearing DEET insect repellent or try some herbs like citronella or lemon eucalyptus. The clothes that is going to be worn should be previously treated with permethrin. Finally, if one sleeps in an open area the bed should be surrounded by a bed net. The risk of contacting the infection may also be reduced if one takes ivermectin preventatively, especially in highly infested areas.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...