Introduction and General Data
Malaria is an infectious disease that is transmitted by a mosquito bite. The parasite that is present in mosquito's saliva enters the blood stream and causes the infection. There are several parasites that are possible threat to humans. Among then is Plasmodium falciparum. The parasite may lead to certain complications. However not all the patients ill with malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum develop complications. Only 1 % of all infected people suffer consequences of the primary infection and among them cerebral malaria is responsible for majority of death outcomes. There are people who are prone to complications and these includes all those older than 65 especially women. Pregnant women are amazingly susceptible for complications of falciparum malaria. Additionally complications affect more people with impaired immune system and those with additional diseases.
Complications
In extremely severe cases patients may end up with cerebra malaria, pulmonary edema and acute kidney or liver failure. Life-threatening anemia together with bleeding or only one of these is another possible complication. As far as metabolic complications are concerned a patient may experience low levels of sugar in blood and acids. Acidosis develops as a consequence of decreased blood volume. The problem is that each of these complications can progress quickly and soon lead to death.
As for general appearance that may point to possible development of complications doctor must pay attention to whether the patients are prostrated, lose consciousness have increased body temperature or develop jaundice.
These serious complications usually affects children under the age of five in those regions of the world where malaria is endemic. Elderly people in Africa die more than children. On the other side the children are more susceptible to permanent neuro-cognitive changes. Seizures and increased intracranial pressure is what affects children most in cases of cerebral malaria. Adults are on the contrary mostly affected by acute kidney failure and edema of the lungs. Acute respiratory distress syndrome is another possible complication of falciparum malaria.
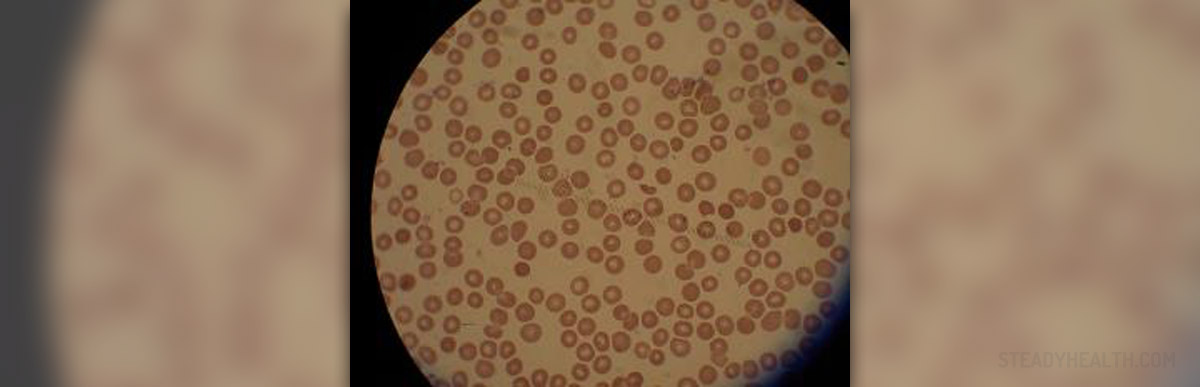
Among all the complications patient can develop thrombocytopenia. This is drop in platelets count. This conditions is followed by increased levels of bilirubin, anemia and even liver enzymes are rather high. White blood cells may be normal or slightly decreased. The laboratory indicator of infection such as C reactive protein and fibrinogen are elevated. Even procalcitonin which is responsible for calcium homeostasis is high. These laboratory parameters are significant indicators of possible occurrence of fatal complications.
Cerebral malaria may result in coma. Convulsions in cerebral malaria can be frequent, repeated and generalized. Malarial retinopathy is another possible complication of this parasitic infection. If this condition affects a patient there is high chance he or she will develop malarial coma.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...