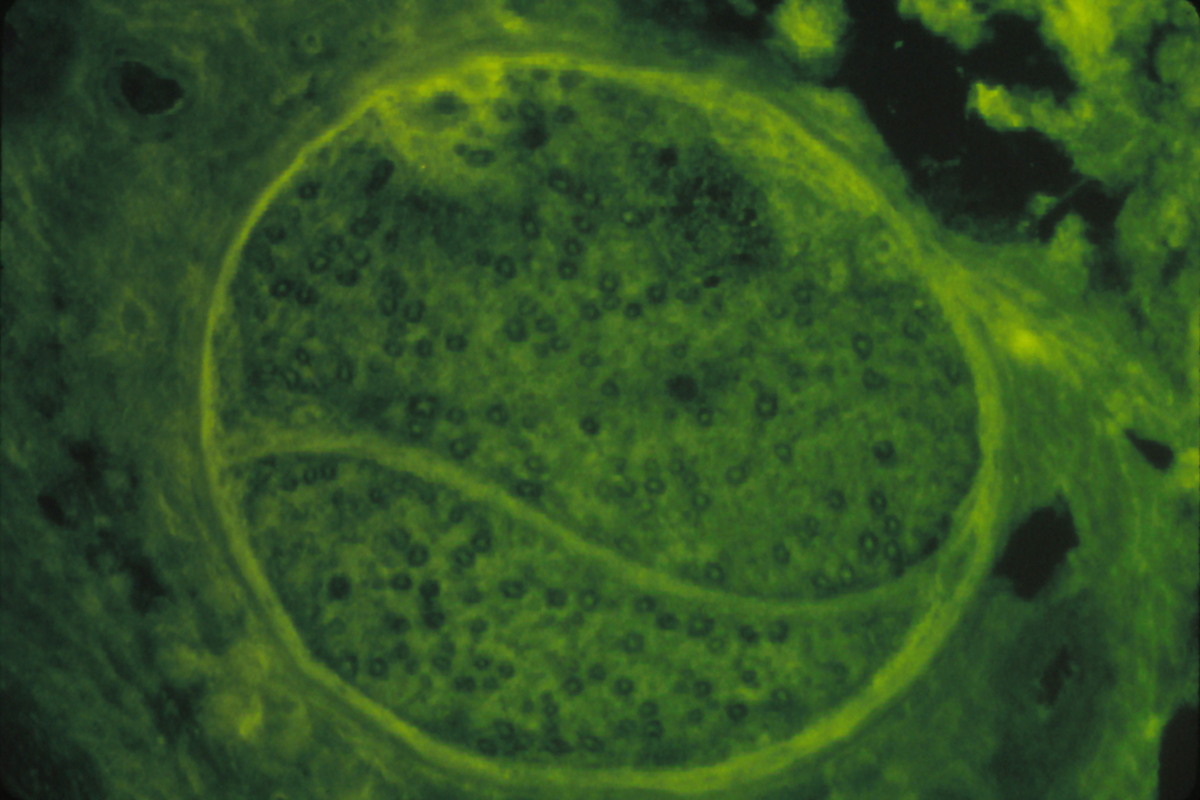
Peripheral neuropathy is a medical term that describes damage to nerves of the peripheral nervous system. The damage is usually caused by diseases of the nerve or from side-effects of systemic illness, traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic problems and exposure to toxins. Most commonly, peripheral neuropathy is caused by diabetes. Peripheral neuropathy usually causes numbness and pain in patient’s hands and feet, with a typical sensation of tingling or burning. Patients often describe this feeling as if they wear a thin stocking or glove. The problems occur because of the inability of nerves to carry information to and from the brain and spinal cord. However, in most patients symptoms of peripheral neuropathy improve with time, especially if they are caused by some other underlying condition that can be treated.
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy
Dysfunctions of peripheral nerves manifest as problems in any of the normal peripheral nerve functions. The loss of sensory function includes symptoms such as numbness, tremor and gait abnormality. These symptoms are commonly accompanied with tingling, pain, itching and crawling. Patient’s skin may become hypersensitive and the pain can be so severe to require use of painkillers.
The loss of motor function includes symptoms like weakness, tiredness, heaviness and gait abnormalities. These symptoms are commonly accompanied with cramps, tremor and muscle twitches.
Causes of peripheral neuropathy
A number of different factors may cause peripheral neuropathy. Some of the causes affect only nerves that relay information from the nervous system to the muscles and organs. The others are responsible for malfunctions in nerves that relay information from the skin, joints and organs back to the brain. In many cases the real cause isn’t obvious as many different factors can cause neuropathies. These factors include: trauma or pressure to the nerve, diabetes, deficiency in vitamin B, E or niacin, alcoholism, infections, autoimmune diseases (such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis and Guillain-Barre syndrome), inherited disorder, tumors, and exposure to poisons.
Treatment of peripheral neuropathy
Treatment of peripheral neuropathy may focus on treating the underlying condition (if present), or relieving the painful symptoms of the disease. If alcoholism causes patients problems with neuropathy, the patient will be advised to restrain from alcohol. Doctors may often recommend physical therapy, occupational therapy and different orthopedic interventions to increase muscle strength and control. Treatment often includes pain relievers, anti-seizure medications and lidocaine patches. Antidepressants are commonly used in treatment, as they have been found to help relieve pain by interfering with chemical processes in the brain.











-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...