
Peripheral Neuropathy OverviewPeripheral neuropathy is a term that collectively refers to conditions marked by damage to the peripheral nerves. The peripheral nervous system includes the nerves that connect the spinal cord and the brain to the rest of the body. It is composed of three main types of nerves: automatic nerves, sensory nerves and motor nerves. Each type of nerves regulates a different function. Any of these nerves can be affected by peripheral neuropathy resulting in different symptoms. Motor neuropathy can impair movement. Autonomic neuropathy is a life-threatening condition as it can affect breathing. Sensory neuropathy can cause loss of sensation.
Peripheral nerve cells are made of three main parts: cell body, axons and dendrites. Peripheral neuropathy most commonly affects axons but other parts of the nerve can be affected too. The axons are surrounded by myelin sheath that transmits signals to the brain.
Causes and Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy can be inherited or acquired. The condition commonly occurs due to trauma to the peripheral nerve, diabetes, alcoholism, vitamin deficiency, tumors and exposure to toxins. Infections such as Epstein-Barr, AIDS, shingles, hepatitis C and Lyme disease can also lead to peripheral neuropathy. Autoimmune disease like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can too cause peripheral neuropathy. Kidney and liver disease as well as hypothyroidism can lead to peripheral neuropathy. Finally, the condition may result out of use of certain medications and inherited disorders like amyloid polyneuropathy. However, many times peripheral neuropathy develops due to unidentified cause and it is known as idiopathic peripheral neuropathy.
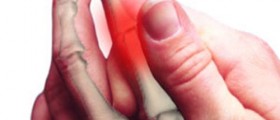
Peripheral neuropathy commonly causes numbness and tingling in hands and feet, sharp and burning pain, increased sensitivity to touch, muscle weakness and loss of coordination in the affected part of the body.
Treatment for Peripheral Neuropathy
Treatment for peripheral neuropathy depends on the underlying cause. The treatment should be prompt in order to prevent permanent nerve damage. The treatment also aims to relieve the symptoms. The pain can be reduced with medications, injections and physical therapy. Sometimes, peripheral neuropathy can be treated surgically.
Medications used for treatment of peripheral neuropathy include pain killers, antidepressant and anticonvulsants. Commonly prescribed antidepressants are tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). These medications may cause side effects such as nausea, constipation, dizziness and poor appetite.
Anti-seizure medications or anticonvulsants like gabapentin and topiramine are often given to treat nerve pain. These drugs may cause nausea, vomiting, drowsiness and dizziness.
Injection therapy is often combined with medications and physical therapy. Commonly used medicine lidocaine is injected into the affected area to relieve the pain.
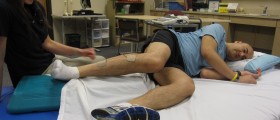
Physical therapy including exercise, massage, electrical stimulation and heat therapy and acupuncture can also be used in treatment of peripheral neuropathy to manage pain, weakness, decreased range of motion and poor balance.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...