
Diabetic neuropathies are disorders that are associated with diabetes. People who suffer from diabetes can develop damage to the nervous system throughout the body and cause symptoms like: numbness or reduced ability to sense pain or temperature changes, tingling sensations, sharp pain that gets worse at night, difficulty walking, weakness in muscles, bone and joint pain. Condition may spread to every organ of the body together with the digestive tract, heart, and genitalia.
Causes
Diabetic neuropathy is a common serious complication of diabetes that affects around 50% of patients. There are certain risk factors that make patients more suitable to develop neuropathy: inadequate blood sugar, blood fat and blood pressure control; overweight patients; people who suffer from diabetes more than 25 years; people over the age of 40; patients diagnosed with kidney disease; smoking or alcohol use.
Symptoms
Some people may not experience any symptoms at all. It depend on the type of neuropathy and kind of the affected nerves. Numbness, tingling, or pain in the feet is regularly the first signal of disease. Symptoms are often negligible at first and damage develops over several years, so it may be undetected for a long time. Possible signs and symptoms often include:
numbness, itching, or ache in the toes, fingers, feet, legs, hands, and armswasting of the muscles of the feet or handsdigestive disorders, nausea, or vomitingdiarrhea or constipationfaintness due to a drop in postural blood pressureurinal problemserectile dysfunction impotence or vaginal drynessweaknessTypes of Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathies divides in peripheral, autonomic, proximal, and focal neuropathy.
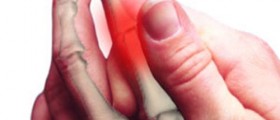
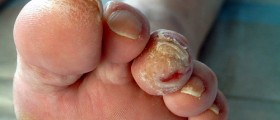
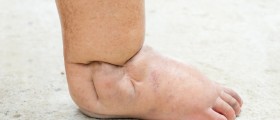
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common form and it causes pain or loss of feeling in the toes, feet, legs, hands, and arms. This condition affects the ends of the nerves first, and nerve endings are situated in feet, legs, hands and arms. Symptoms of the peripheral neuropathy often worsen at night. It causes weakness in muscles that may lead to problems in walking. Foot deformities, hammertoes, blisters and sores as well as the other type of foot injuries may occur.
Autonomic neuropathy causes changes in autonomic nervous system that controls the heart, bladder, lungs, stomach, intestines, sex organs and eyes. Damage to the body caused by autonomic neuropathy may also lead to hypoglycemia unawareness, a condition in which people no longer experience the normal symptoms of low blood sugar levels.
Proximal neuropathy affects nerves closer to the thighs, hips, or buttocks. It affects legs most often but it may as well spread to arms and abdomen. Signs of neuropathy are usually being felt in one side of the body, though it may spread to both sides, too.
Focal neuropathy is damage of one nerve, or a group of nerves, causing muscle weakness or pain. It strikes suddenly usually the nerves in the arm, leg or face. Symptoms often withdraw in a couple of weeks.
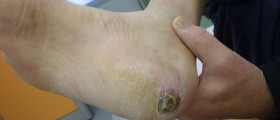
Foot Care
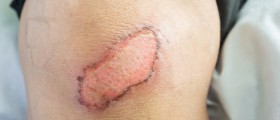
General foot care tips should be specially applied to people with neuropathy. Loss of sensation in the feet means that serious injuries can go overlooked, the infection might extend as far to the bone and the foot may have to be amputated. Nearly half of the amputations is being caused by neuropathy. The worse possible outcomes could be prevented only by careful and regular foot care.
People with diabetes should be taught how to examine their own feet and how to identify the early signs of diabetic foot problems. They should always wear the appropriate shoes to protect the feet of injuries. If wearing new shoes they should adapt to them gradually, wearing them only for a short time at first.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...