At this moment, there are a lot of people in the United States who suffer from various digestive problems. There are so many different digestive problems that it is hard to even begin identifying the possible cause. You could suffer from different kinds of gastrointestinal infections, some of which could go away very quickly. Others, however, like inflammatory bowel syndrome, are known to last for a very long period of time.
All illnesses that cause chronic inflammation in the intestines are considered to fall under the category of inflammatory bowel syndrome or IBD. If you suffer from diarrhea, stomach cramps, abdominal pain, or many of the other symptoms associated with the stomach, you might want to find out everything you can about IBD. So, what exactly do you need to know about IBD or Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
What exactly is (IBD) Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
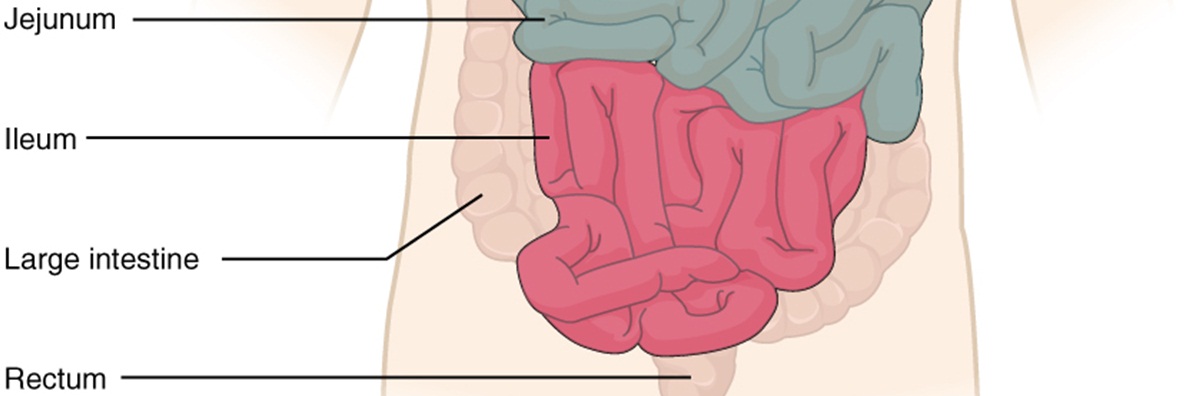
Every person most likely knows that the digestive system contains organs whose main role in the digestive system is to help you digest your food properly and absorb all the important nutrients from the food you eat. The small and large intestines are probably two of the most important parts of the digestive system in your body. It’s important people are aware that just like any other organ in the human body, your intestines can develop different types of disease.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is known to cause other, more severe, problems than diarrhea and stomach cramps. In fact, IBD can even cause delay in puberty or growth problems in some cases. The main reason this happens is because the body needs nutrients, and in this case, the body does not receive all the essential nutrients.
There are actually two different types of IBD, the two biggest types being Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. A person may notice that he or she is suffering from Crohn’s disease by paying attention to a variety symptoms including abdominal cramps and pain, diarrhea with blood in the stool, a fever and weight loss. A person with this illness will also feel extremely tired and experience a loss of appetite. On the other hand, people who suffer from ulcerative colitis may notice abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea as two of the most common signs.
There are several factors that have been postulated to have an effect on the development of this group of diseases, which include but are not limited to bacterial contamination, a change in the immune system, and genetic variations. For instance, a mutation in the NOD2 gene is associated with an increase susceptibility to IBD via production of proinflammatory cytokines.
While genetic predisposition plays a key role in immune-mediated diseases, the major influence appears to be due to environmental factors. Indeed, current research suggests that autoimmune diseases are most prevalent in highly industrialized nations but rare in less developed countries. Moreover, studies have shown that increased consumption of milk protein, animal protein, and polyunsaturated fatty acids can increase the risk for IBD, and that consumption of tobacco increases the risk of Crohn’s disease.
- The major subtypes of IBD, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, have a high prevalence rate in the world, with North America noting the highest frequency of people suffering with Crohn’s disease. In addition, statistics show that an estimated 129,000 people live with the disease in Canada.
- Although the onset of the disease usually occurs during adulthood, children are increasingly being diagnosed with IBD.
- Treating IBD often involves use of medications that can diminish the symptoms and decrease the inflammation in the colon lining. A group of anti-inflammatory drugs including 5-aminosalicylic acid is commonly used to treat IBD.
- Other drugs such as infliximab are also indicated in patients who have failed conventional therapy and are hospitalized with severe IBD. Infliximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody against tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-?), a cytokine involved in intestinal inflammation. Several other immunomodulatory drugs, such as thalidomide, can also be used to treat a patient with severe IBD. Formerly used as a sedative and hypnotic, this synthetic drug has been shown to significantly reduce the inflammation associated with IBD.
- While medication is commonly used to treat IBD, most pharmaceutical compounds have side effects such as headache, diarrhea, and nausea, which can reduce patient compliance and result in worsening of the condition. Therefore, appropriate delivery systems must be developed in order to overcome the limitations and issues associated with the currently available treatments for IBD.
- The prevalence of Crohn’s disease is relatively high in highly industrialized countries. Its incidence is five in 100,000 people and its prevalence is estimated to be 30–50 of 100,000 people in western countries.
Apart from these symptoms, some people also experience nausea, tiredness, weight loss and loss of appetite. Some people who suffer from ulcerative colitis may also experience seemingly being completely free of all the symptoms for a while at some point, and then suddenly start experiencing the same symptoms after some time.
Who can suffer from (IBD) Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
Every person can end up suffering from IBD. However, it is most common for people who are in their late teens and twenties to be suffering from it. Both men and women can be affected by IBD. Currently, there is still no known cause of IBD. It’s known you can get IBD if your immune system isn’t working as it should. Genetics, too, are shown to play a part in the cause of IBD.
What can doctors do to treat (IBD) Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
It is important that people go to the hospital if they believe that they may be suffering from IBD. The doctors will perform physical exams and look at the patient’s medical history. After that, certain tests will be performed in order to be decided what the best treatment plan should be. The sooner you receive medical attention, the more quickly you will be able to implement lifestyle changes that will alleviate your symptoms over the long term.
- medlineplus.gov/smallintestinedisorders.html
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000300.htm
- Photo courtesy of OpenStax College by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:2417_Small_IntestineN.jpg














Your thoughts on this
Loading...