What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
Inflammatory bowel disease is a sort of an umbrella term used for different types of medical conditions which are characterized by chronic or recurring inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract due to immune responses. Out of all different sorts of inflammatory bowel diseases, the most common ones include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Although they are completely different, they both trigger a rather abnormal response by the immune system in which the foods and the healthy bacteria get mistaken for harmful substances and then get attacked by white blood cells. All of that leads to inflammation of the lining of the intestines and all the other common symptoms of the inflammatory bowel disease. It is also important to note that the aforementioned medical conditions often get confused with another medical condition called irritable bowel syndrome.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
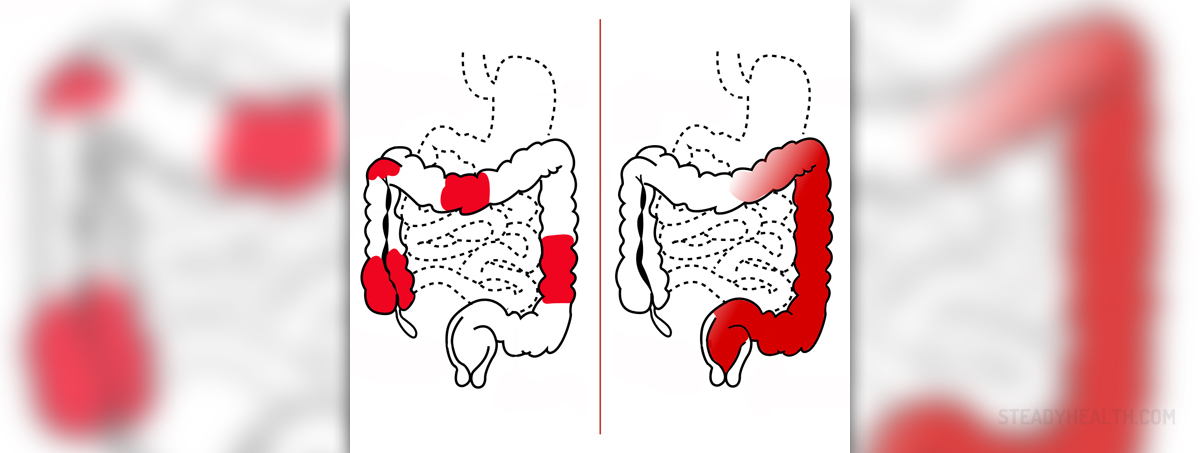
Ulcerative colitis is a certain type of gastrointestinal disorder which only affects the colon. It does not affect any other part of the gastrointestinal tract. The condition is initially characterized by loosening of the stool which often can be bloody as well. Such loose stool may also sometimes be accompanied by several other common symptoms such as severe urgency to have a bowel movement and cramping abdominal pain. Bouts of diarrhea may be sudden or develop gradually. Due to all these symptoms, the patient usually tends to suffer from loss of appetite and weight loss. Fatigue is often experienced in most cases of ulcerative colitis. People who suffer from severely bloody stools may additionally experience the onset of anemia. Other less common symptoms of ulcerative colitis may include different types of liver disorders, eye inflammation, painful sensation in joints and skin lesions. Most cases of ulcerative colitis are mild in nature, but there are also severe forms of the disease which may involve fever, nausea and intense abdominal cramping. Symptoms of this medical condition tend to come and go on their own. Ulcerative colitis may lead to several complications such as failure to respond to medical treatments, abdominal bloating, colon cancer, rupture of the bowel and deep ulcerations.
Crohn’s disease is much more different than ulcerative colitis mainly due to the fact that it may affect any portion of the gastrointestinal tract. The parts which are usually affected most frequently include the beginning of the large bowel and the end of the small bowel. The most common symptoms of Crohn’s disease include fever, cramping abdominal pain, persistent diarrhea and sometimes even rectal bleeding. There are a large number of cases of Crohn’s disease which involve loss of appetite and subsequent weight loss. A peculiar thing about Crohn’s disease is that it may additionally affect certain other body parts such as the liver, skin, eyes and the joints. It is not uncommon for people who suffer from Crohn’s disease to experience fatigue. As far as complications are concerned, Crohn’s disease may be associated with the occurrence of blockage of the intestines and development of ulcers in the intestines. The blockage is characterized by bloating, vomiting and cramping pain, while the intestinal ulcers may easily transform into fistulas. Crohn’s disease involves a higher risk of colon cancer as well. Diagnosis of both medical conditions usually involves certain methods such as colonoscopy and biopsy of pathological lesions.
Treatment
Ulcerative colitis is commonly treated by utilizing four different classes of medications which include antibiotics, immune modifiers, steroids and aminosalicylates. In spite of that, most cases cannot be treated successfully without any complications. This is why there are a large number of cases of ulcerative colitis which require surgical interventions. Surgery for ulcerative colitis is medically referred to as colectomy and it involves the removal of the colon after which the patient is cured.
The treatment for Crohn’s disease involves even more different types of medications as there are five of them, including biologic therapy, antibiotics, immune modifiers, steroids and aminosalicylates. As it is the case with ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease often requires a surgery in which the affected parts of the colon are removed so that the patient can be cured.
Epidemiology
Inflammatory bowel disease usually affects those who are between 15 and 30 years of age, but it can actually occur at any age. Crohn’s disease affects women much more than men, while with ulcerative colitis the situation is completely different because it affects men more than women. Smokers get affected by inflammatory bowel disease more than those who do not smoke. Inflammatory bowel disease is frequently reported in the developed countries while the number of cases associated with the same disease is not so high in countries which are not developed yet.
Prognosis
The biggest problem of those who suffer from inflammatory bowel disease is that the quality of their lives is largely affected by the symptoms of the condition which usually tend to be rather socially unacceptable. The disease is not that dangerous on its own, but it can lead to further medical complications which sometimes may even be fatal.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...