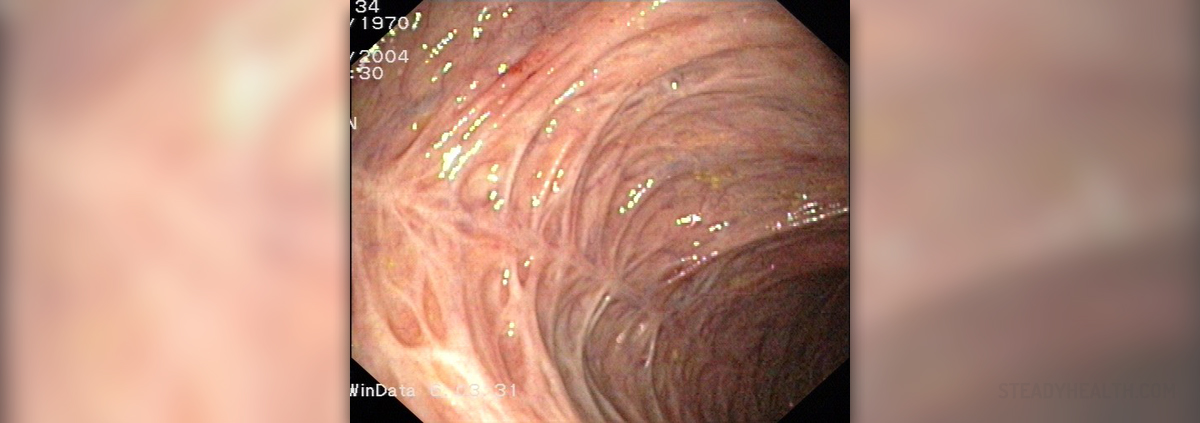
IBS
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) may be easily mixed up with the microscopic colitis or mastocytic enterocolitis, because of the similar symptoms. The only way to diagnose microscopic colitis and mastocytic colitis are biopsies and sometimes special coloring, which aren’t the standard procedures for most doctors.Diagnostic Procedures - Biopsy
Colon biopsy should be a necessary procedure in patients suspected to suffer from irritable bowel syndrome. Biopsy of the microscopic colitis will show the increase of immune or lymphocyte white blood cells (intraepithelial lymphocytosis) or a buildup of collagen in the lining of the colon. At the same time, the surface of the colon would look normal.Mastocytic enterocolitis is a subtype of microscopic colitis, known to show the increase of mast cells in the lining of the intestine. These changes are visible only under a non-standard, special stain.Diagnostic Procedures – Multiple Biopsies
Patients experiencing diarrhea, abdominal pains, bloating and gases should be biopsied several times. The repeated biopsies are necessary because the inflammation and irritation could be present in patches of the intestine, so the multiple biopsies should enable a specialist to properly diagnose the cause of these symptoms.Diagnostic Procedures – Blood Tests
To diagnose the condition, doctors will screen the patients for ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease and Celiac disease. These blood tests and biopsies of the intestines are important for the exact diagnose and treatment of this condition, whether it is the IBS or microscopic colitis.Treatment
Under the microscope, celiac disease and microscopic colitis are seen as the increase of lymphocyte cells. The disorders are confirmed once there are 20 or more lymphocytes per 100 of epithelial cells. Recent studies have shown the connection between the gluten injuries and the decrease of lymphocytes in the intestines. Therefore, patients suffering from the microscopic colitis usually respond to the diet without gluten. Some specialists recommend the testing for gluten sensitivity and gluten-free diet for people diagnosed with IBS.IBS could also be misdiagnosed in patients suffering from the non-celiac gluten sensitivity, collagenous or lymphocytic colitis.
IBS can’t be treated, except for the anti-diarrhea and anti-spasm medications. People often tend to cope with their problems, such as abdominal pains and diarrhea, not aware that the diagnosis might be wrong. Even though the doctors suggest increasing the intake of fibers in their diet, it might also prove to be unsuccessful. Some of these people suffering from these diseases may develop secondary problems, like autoimmune disease, osteoporosis, iron deficiency or infertility.
Possible treatment could be food without gluten, which is proven to help easing the symptoms in people suffering from IBS, celiac disease and microscopic colitis.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...