Crohn’s disease is a chronic disease characterized by the inflammation of the digestive or gastrointestinal tract. Crohn’s disease most commonly affects the lining of the small and large intestines. However, this disease can cause inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus.
Crohn’s Disease Overview
Crohn’s disease was first described by and later named after Dr.Crohn. Crohn’s disease is also known as granulomatous enteritis or colitis, regional enteritis, ileitis or terminal ileitis. The disease is similar to ulcerative colitis which causes inflammation of the superficial layers of the lining of the large intestine.
Neither Crohn’s disease nor ulcerative colitis can be cured. Both diseases are chronic and cause episodes in which symptoms flare up followed by periods of remission in which symptoms disappear.
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis belong to a group of disorders called inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Between 500,000 and 2 million people in the United States are diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease. IBD equally affects males and females and may occur in people of all ages.
However, irritable bowel disease most commonly affects individuals aged between 15 and 35 years. Also, American Jews of European descent have 4 to 5 times more chances to develop the disease than general population. On the other hand, African Americans as well as Hispanic and Asian populations have lower risk for IBD.
Crohn’s disease is more likely to develop in individuals with family history of the illness. In fact, many patients with Crohn’s disease have a relative with Crohn’ disease or some other form of irritable bowel disease.
Causes of Crohn’s Disease
Exact cause of Crohn’s disease is not identified. Researchers believe that infection by certain bacteria such as strains of mycobacterium can lead to Crohn’s disease. It has been observed that individuals suffering from irritable bowel disease have abnormal functioning of the immune system.
The immune system is made of proteins that protect from infections and immune cells that produce these proteins. Individuals with IBD have overactive immune response in which immune cells mistakenly attack lining of the intestines. This finally leads to chronic inflammation and ulceration.Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
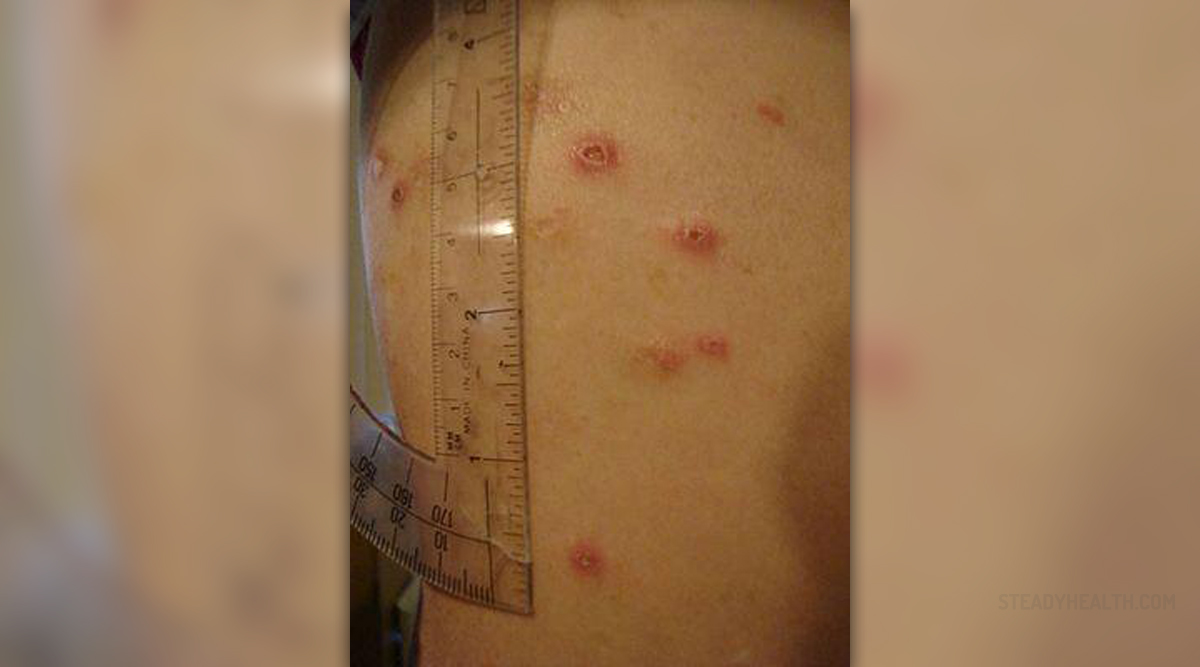
At first, Crohn’s disease causes small and shallow ulcerations on the lining of the bowel. Over time, the erosions develop into ulcers. As the disease progresses, the bowel becomes narrowed and may eventually get obstructed. Sometimes, deep ulcers can rupture the walls of the intestines creating a tunnel between the intestine and nearby organs. This can result in different complications.
The main symptom of Crohn’s disease is diarrhea. Cramping, abdominal pain and rectal bleeding are common too. Other symptoms include reduced appetite, weight loss, skin disorders, fever and arthritis.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/crohns-disease/
- medlineplus.gov/crohnsdisease.html
- Photo courtesy of Crohnie by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Crohnie_sores_4.JPG















Your thoughts on this
Loading...